Sauna Heaters
Saunas are a popular method of heat and humidity therapy used by people for thousands of years for therapy, relaxation and body detox. One of the main components used to keep the interior of the sauna warm and achieve the desired temperature is sauna heating elements.
Isıer Rezistans offers you a unique service with its specially designed resistances to turn your sauna pleasure into a warm and comfortable experience.
What are Sauna Heaters?
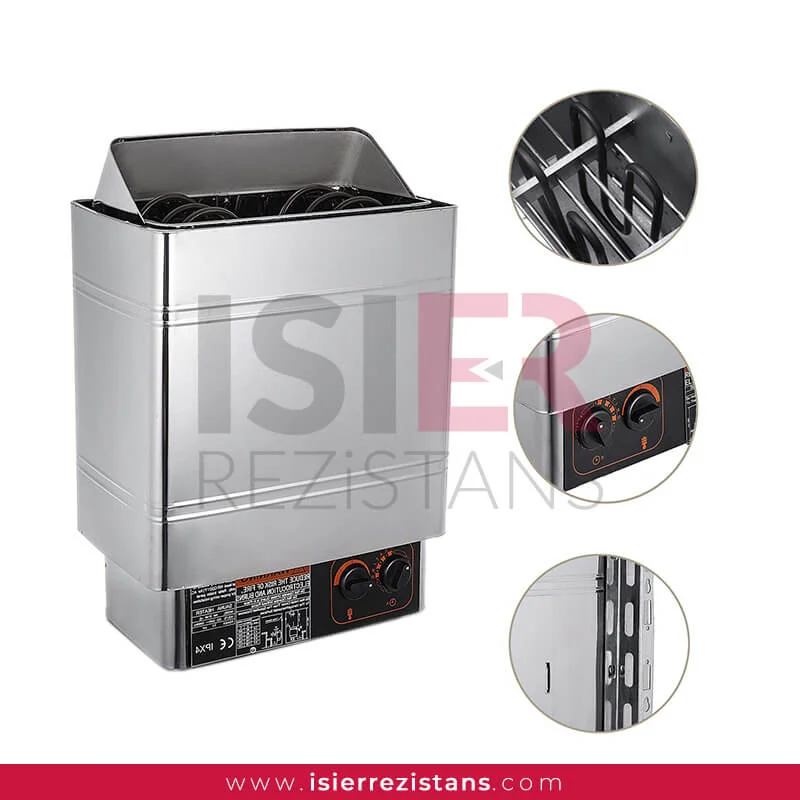
Sauna heaters are heating elements that heat the stones inside the sauna, allowing the environment to reach the desired temperature and humidity levels. These heaters are designed with special materials to provide safe and effective heating in the sauna environment.
Isıer Heater’s sauna heaters are an ideal choice to enhance your sauna experience and relax in a warm atmosphere. With reliable, durable, and long-lasting sauna heaters, Isıer Heater continues to offer its customers a unique sauna pleasure.
What are Sauna Heater Technical Specifications?
The technical specifications of sauna heater elements include various parameters that determine the performance of these specialized heating components. Here are the detailed technical specifications of sauna heater elements:
Material: Sauna heater elements are typically made of materials resistant to high temperatures. Stainless steel, nickel-chromium alloys, or titanium-based materials are commonly preferred.
Power Capacity: The power capacity of sauna heater elements determines how much heat they can generate in a specific period. This value is expressed in watts (W), such as 3000W or 6000W, for example.
Voltage and Current Values: The operating voltage and current values of the heater are specified. These values are important to ensure compatibility with the electrical system used. For instance, 220V or 380V.
Size and Shape: Sauna heater elements can be manufactured in various sizes and shapes. The length is usually specified in millimeters (e.g., 400mm or 600mm).
Resistance Value: The resistance value of the heater is expressed in ohms. This value determines how much resistance the heater exhibits under a specific voltage.
Temperature Range: The operating temperature range of sauna heater elements is specified, typically in Celsius degrees (°C). For example, 0°C to 120°C.
Protection Class (IP Rating): The IP class indicating the resistance of the heater to water and dust is specified. For instance, IPX4.
Connection Type: The connection type for mounting the sauna heater element inside the sauna is specified. It could be threaded, flanged, or other special connection types.
Heating Element Type: Depending on the design of the heater, it could be of different types such as steam-tube, immersion type, or coil.
Control and Regulation: Some sauna heater elements come with an integrated control unit or thermostat. This control unit is used to precisely adjust the sauna temperature.
Special Coatings and Materials: Some heaters may be coated with special coatings or materials to enhance durability or adapt to specific conditions.
Ease of Installation: Sauna heater elements should be easy to install. Options for mounting may include threaded, flanged, or other mounting options.
These technical specifications indicate that sauna heater elements are designed to meet various application needs and can be integrated into sauna models or usage purposes accordingly.
What Do Sauna Heaters Do?
Sauna heaters are heating elements used to keep the interior of the sauna warm and maintain the desired temperature level. The basic functions of sauna heaters are as follows:
Heating the Stones Inside the Sauna: Sauna heaters typically heat special sauna stones placed inside the sauna, raising the temperature of the environment. These stones retain heat for a long time and provide homogeneous heat distribution within the sauna.
Temperature and Humidity Control: Sauna heaters assist in controlling the temperature and humidity levels inside the sauna. This allows users to personalize their sauna experience and achieve their desired comfort levels.
Relaxation and Therapy: Sauna heaters offer users a range of health benefits through the high temperatures and low humidity levels created within the sauna environment. These benefits include muscle relaxation, toxin elimination, and overall relaxation.
Contribution to Sauna Rituals: Some saunas are designed for special sauna rituals and ceremonies. Sauna heaters help achieve the appropriate temperature and humidity levels for these rituals.
Increasing Circulation: High temperatures in the sauna can increase blood circulation within the body, aiding in toxin elimination. Sauna heaters are designed to contribute to these health benefits.
Stress Reduction and Mental Relaxation: The sauna experience, with its high temperatures, can increase endorphin release in the body, reducing stress and promoting mental relaxation. Sauna heaters are essential to support this relaxation experience.
Safe and Effective Heating: Sauna heaters are designed to provide safe and effective heating for users. Using materials and designs compliant with safety standards, sauna temperature is kept under control.
Sauna heaters are an important component widely used in healthy living practices and personal care rituals. The sauna experience is a relaxation and therapy method that offers positive effects on both physical and mental health.
In Which Sectors Are Sauna Heaters Used?
Sauna heaters are heating elements primarily used in saunas and similar spa facilities. Therefore, sauna heaters are predominantly found in the health and beauty industry, accommodation facilities, and personal care centers. Here are the industries where sauna heaters are commonly used:
Sauna and Spa Facilities: These facilities offer customers a relaxing sauna experience with temperature and humidity control provided by special sauna heating systems, including sauna heaters.
Hotels and Accommodation Facilities: Luxury hotels, resorts, and spa rooms may use sauna heaters to offer guests private sauna facilities.
Fitness and Sports Centers: In spa or wellness areas of fitness facilities, sauna heaters can provide an additional option for relaxation and regeneration for athletes and fitness enthusiasts.
Beauty and Wellness Centers: Beauty salons and wellness centers may equip sauna rooms with sauna heaters to offer clients heat therapy and promote healthy skin.
Health Clubs and Associations: Health clubs and similar membership-based facilities may use sauna heaters to offer members a healthy lifestyle and relaxing environment.
Home and Personal Sauna Applications: Private home saunas or personal spa areas can provide individuals with a healthy sauna experience using sauna heaters.
Hospitals and Healthcare Institutions: Rehabilitation centers or healthcare institutions may use sauna heaters to offer sauna therapy as part of treatment plans.
Tourist Facilities and Thermal Hotels: Hotels and thermal facilities in tourist areas may use sauna heaters to offer customers a thermal spa experience.
Entertainment and Lifestyle Centers: Health and entertainment areas in large shopping malls or entertainment complexes may offer spa facilities equipped with sauna heaters.
In these industries, sauna heaters are typically used to provide customers with health, relaxation, and a luxurious experience. These heating elements can be customized according to different types of businesses and customer needs and are available in various sizes and power capacities.