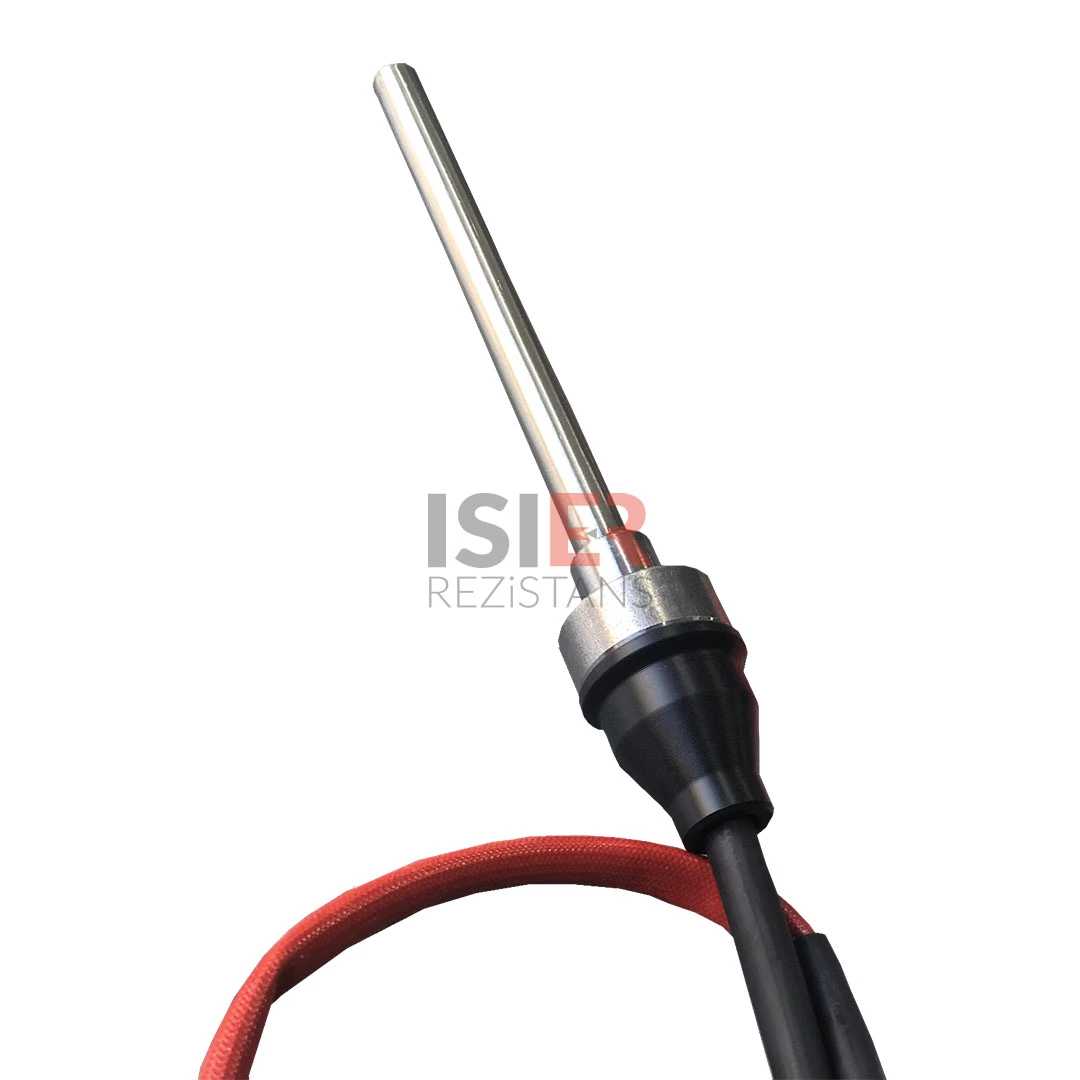
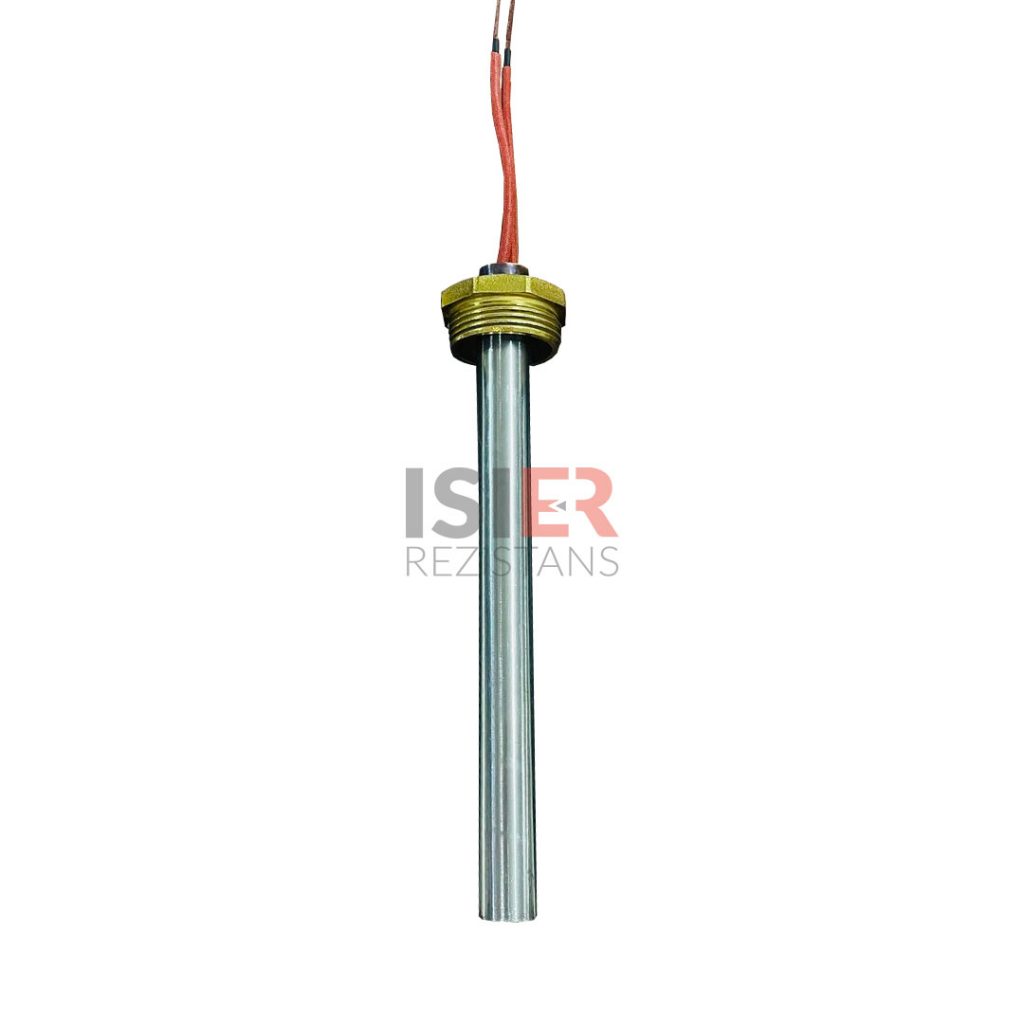
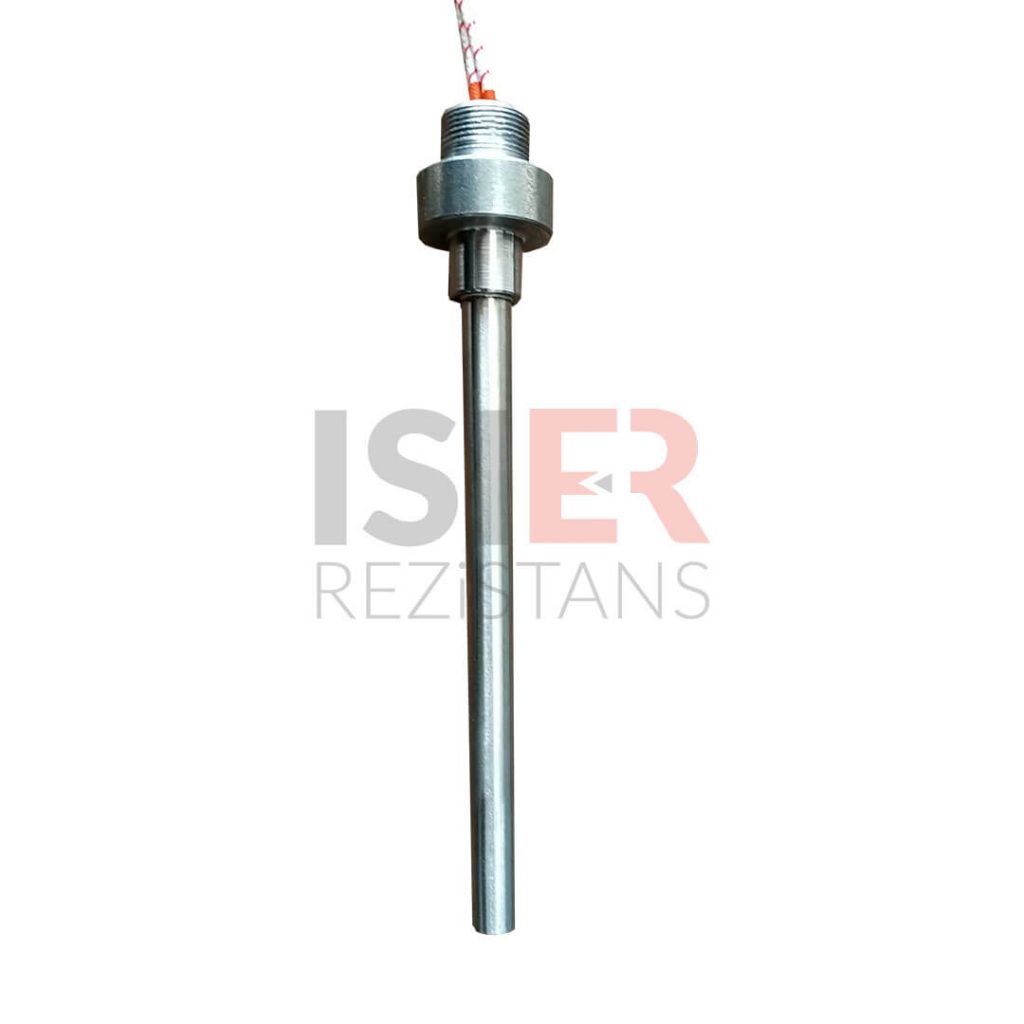
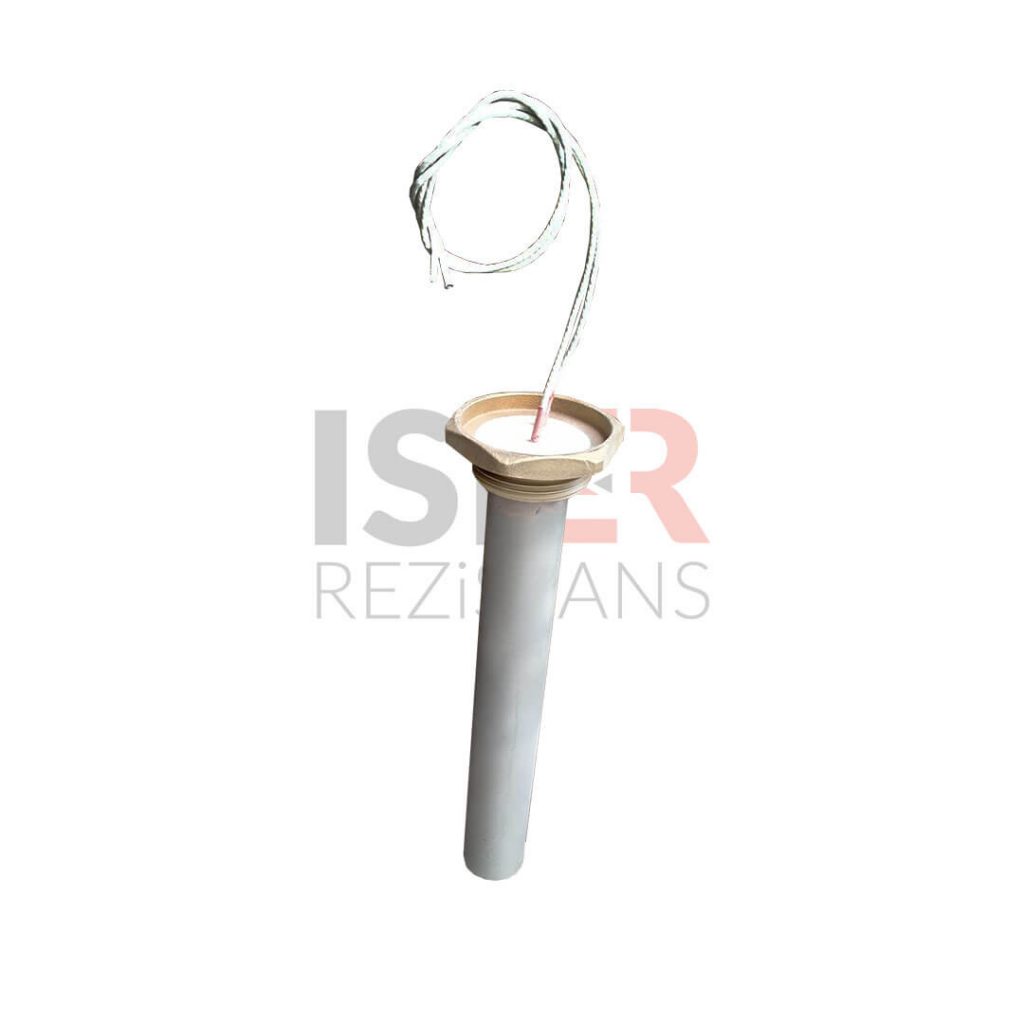
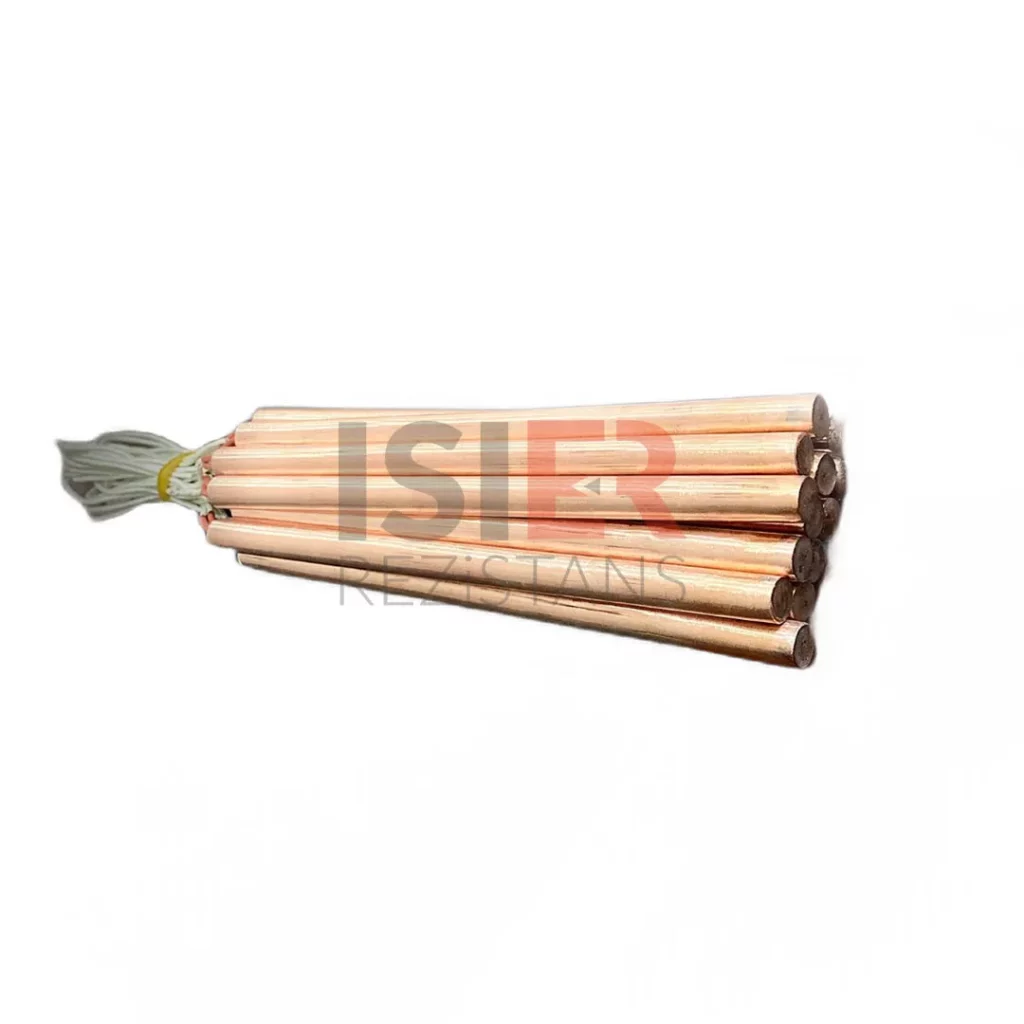
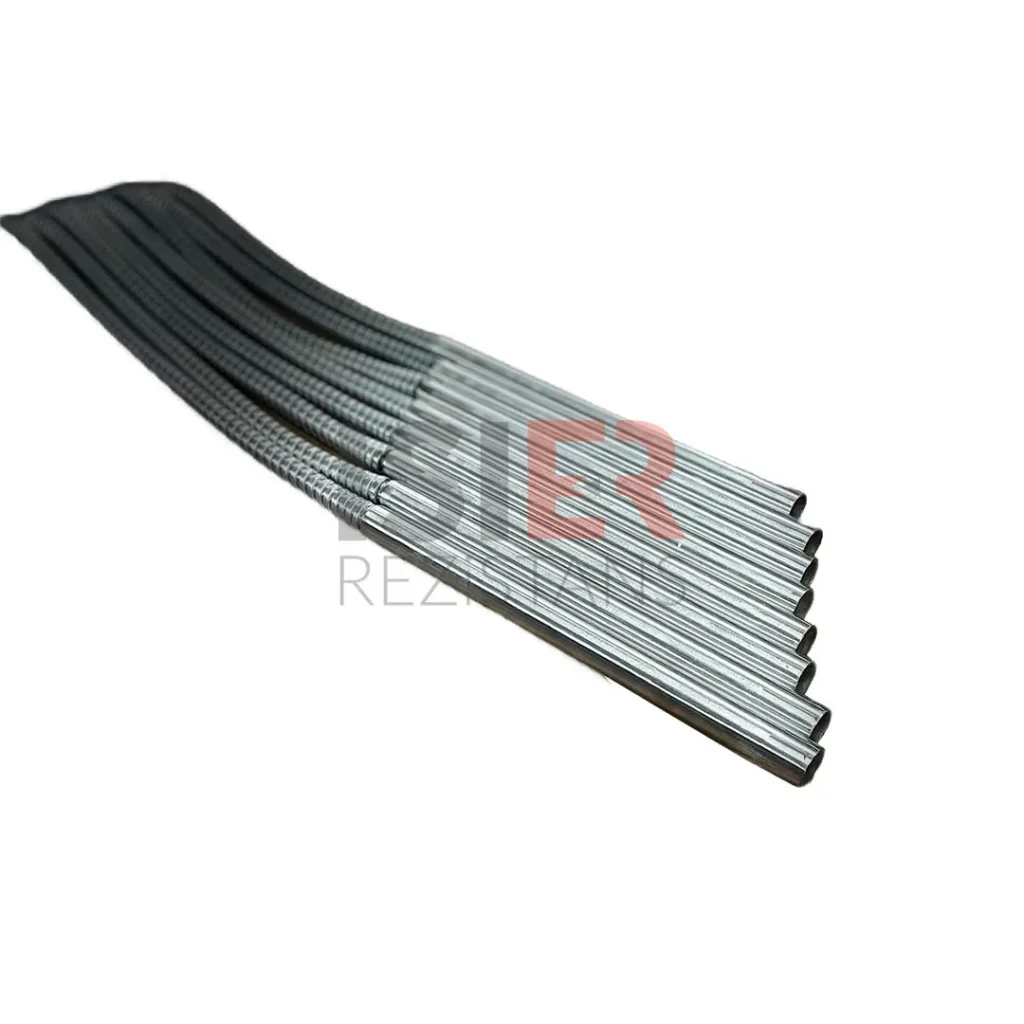
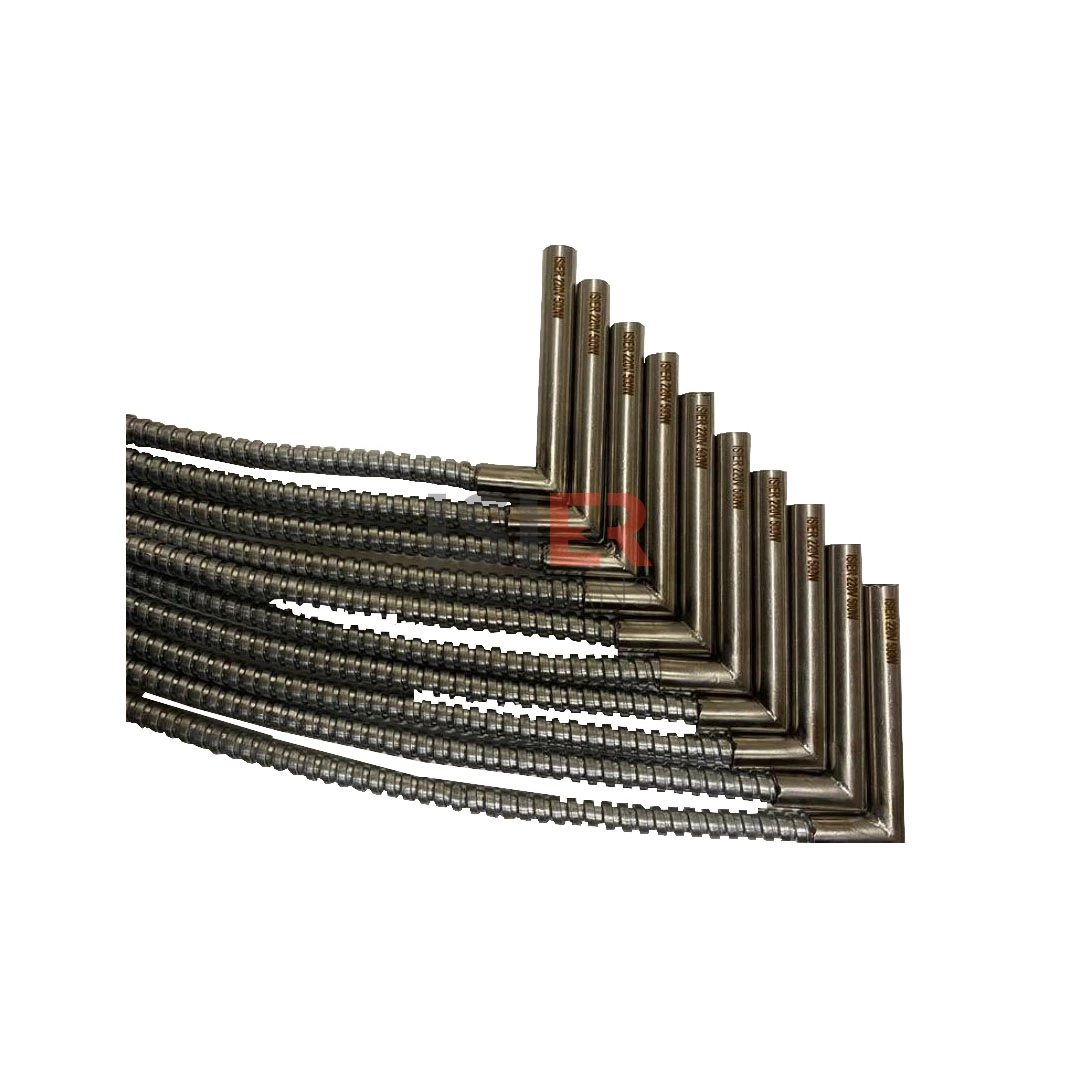
Cartridge Heaters
Carthidge Heaters are widely used in many areas today and are the most preferred type of resistance, especially in the heating of molds and presses. In addition,is the high quality Resistance type preferred for heating the jaws of packaging and packaging machines and heating water, oil and corrosive.
create strong heating by using high watts in small areas and molds that require electric heating, thus providing excellent heat in harsh conditions operating conditions.These resistors can produce heat very quickly due to the thinness of magnesium oxide powder between the wire and the pipe sheath. In addition, the heat generated in this system is extremely efficient and a high temperature can be obtained using very little energy.
Technical Information
are one of the most preferred types of resistance in industrial areas. Flare resistors, which are frequently used in rubber and plastic processing, food, chemistry, wood and many other fields, are among the most preferred products recently. Carthidge Heaters produced in different watts meet the expectations of our customers easily with both quality and easy integration. The flare resistance, which has easy-to-assemble properties, is very pleasing to its users in terms of price-performance.
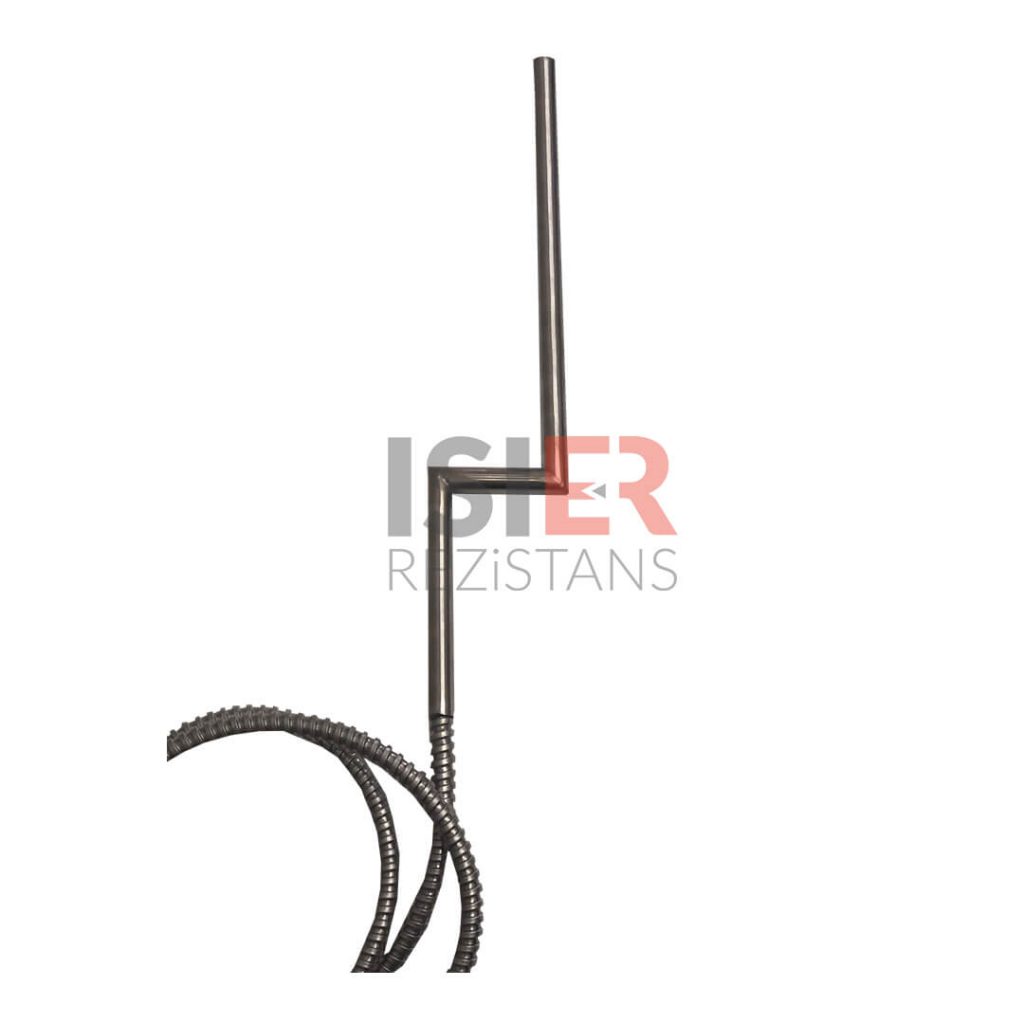
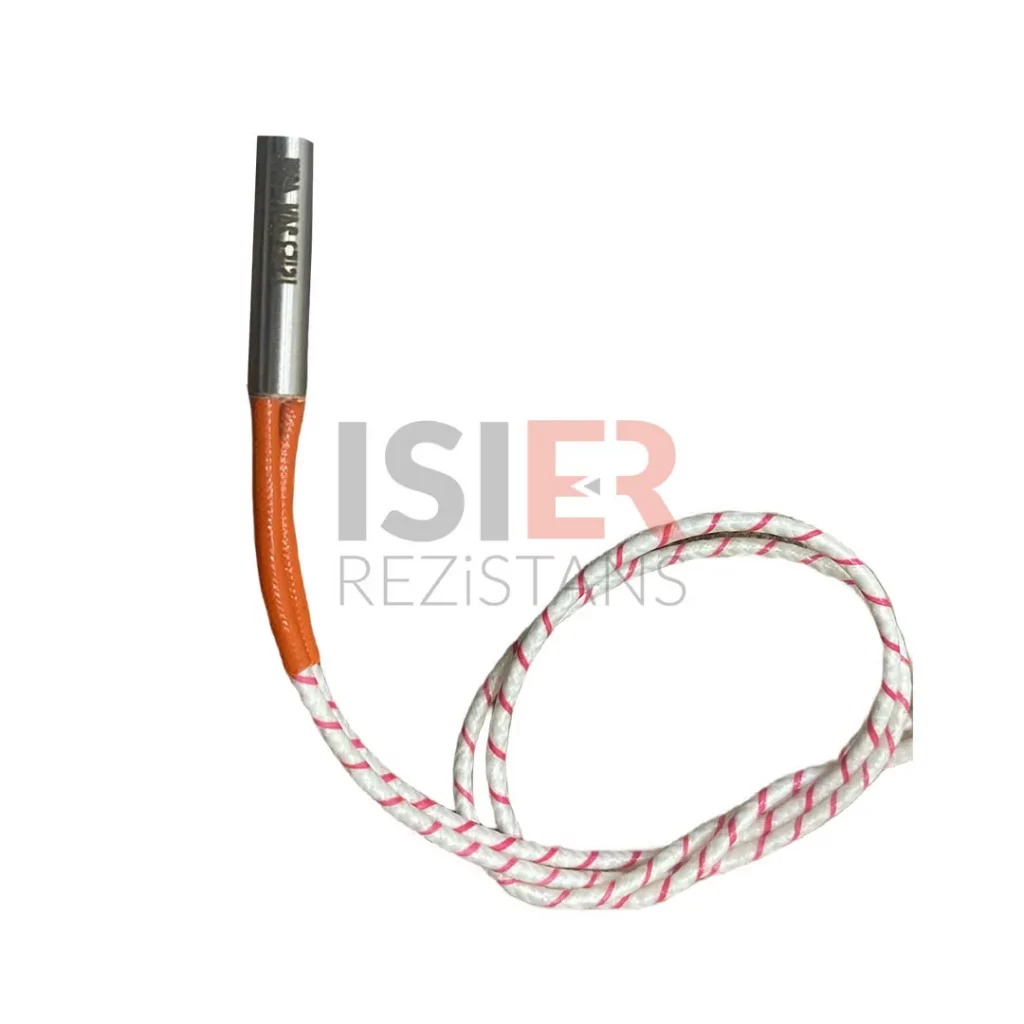
Carthidge Heaters can be produced from 4mm to 31.5mm in pipe diameters. The height size can be produced from a minimum of 30 mm to 5000mm. In addition, it can be produced as L type, elbowed, Cubed elbow, Steel Braided Armored, Spiral Armor Protected, glanded, flanted, sleeved with 90 °C bend. Flare Resistors are produced using 80/20 chromium nickel resistance wire, wrapped in the same equation and at frequent intervals in maximum values, according to the normal values of other resistors.An even heat dissipation is ensured thanks to magnesium oxide used in flare resistors. Manufacturing is carried out using standard CR-NI 304 quality (stainless) pipe as an external housing. European (French NTSE 3000 (350 C) fiber braided pure nickel cables are used in the electrical cables of the cartridge resistors produced. . In flare resistors, the standard cable lengths are 25 cm and cable lengths can be extended according to the desired dimensions if desired.
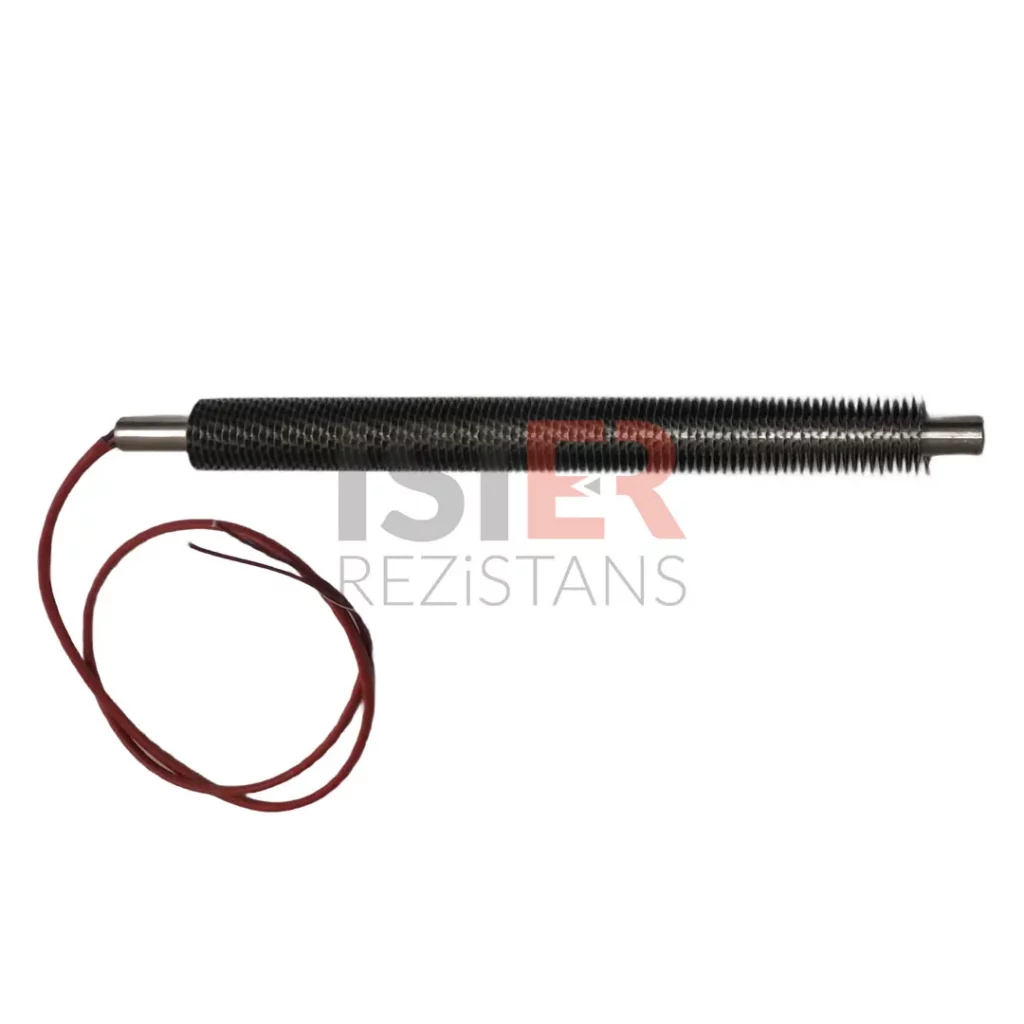
These resistors are produced using stainless steel material in many options according to the place of application. In addition, stainless steel can be produced. With the latest technology, the production of tubular flare type resistors is also easily realized. Flat tubular Flare Type Resistors are widely used for heating various liquids and horizontal plates and presses.
Parts of high wattage flare resistors create a strong heating in environments and molds where heating is required. In this way, it ensures excellent heat, especially in industrial working conditions requiring high heat.
What is Cartridge Heaters?
Cartridge Heaters is a term used to determine the flare temperature of a metal material. This value prevents the metal material from catching fire or burning if the metal material has a high flammability temperature.
What Does Cartridge Heating Resistor Do?
Cartridge heaters are used to enhance fire safety and prevent materials from igniting. For instance, when automatic extinguishing systems are designed to prevent materials from catching fire in the event of a fire, it is important for the cartridge heater value to be high. Similarly, materials with high cartridge heater resistance can also be used to enhance the safety of electrical and electronic devices.
Cartridge Heating Usage Areas
Cartridge heaters are important in the following areas of application:
Fire safety: When fire extinguishing systems are designed to prevent materials from igniting in the event of a fire, it is important for the cartridge heater value to be high.
Electrical and electronic devices: Materials with high cartridge heater resistance can be used to enhance the safety of electrical and electronic devices.
Industrial equipment: Industrial equipment requires a high cartridge heater value to prevent ignition and enhance fire safety.
Aerospace industry: Aircraft use materials with high cartridge heater values for fire safety.
Furniture and decoration: Cartridge heater resistance is important in furniture and decoration products to enhance fire safety.
Cartridge Heating Technical Specifications
When the technical specifications of cartridge heater resistance are enumerated with numerical data, the following can be stated:
1. Ignition Temperature: Ignition temperature is a measurement used in determining the cartridge heater resistance value. It is typically measured in Celsius (°C) or Kelvin (K). For example, if a material’s ignition temperature is 200°C, the cartridge heater resistance value indicates that this material has high cartridge heater resistance.
2. Ashing: Ashing is a measurement used in determining the cartridge heater resistance value. It is usually expressed as “yes” or “no.” For instance, if a material’s ashing value is “yes,” the cartridge heater resistance value indicates that this material has low cartridge heater resistance.
3. Material Type: Material type is important in determining the cartridge heater resistance value. Different types of materials (such as polymers, metals, composites, etc.) may have different cartridge heater resistance values.
4. Test Method Used: The test method used in determining the cartridge heater resistance value (such as ASTM E84, BS 476 Part 7, etc.) affects the accuracy and validity of the value.
5. Operating Conditions: Operating conditions (such as heat treatment, mechanical processing, etc.) are important in determining the cartridge heater resistance value. Different operating conditions can lead to different cartridge heater resistance values.
Cartridge Heating
Cartridge heaters are one type of electric heating element. They are commonly used in household appliances, industrial equipment, and heating systems. They derive their name from their appearance, resembling an electric cable plugged into a socket.
The primary function of cartridge heaters is to convert electrical energy into heat energy. When an electric current passes through this resistive element, electrical energy within the resistance material is converted into heat. This heat is then used to warm the environment where the cartridge heater is located.
These types of heaters are commonly employed in various heating systems, such as water heaters, ovens, stoves, grills, industrial furnaces, and similar devices. Their operation principle relies on the high resistance of the resistive material and its ability to convert electrical energy into heat. Cartridge heaters are preferred in many applications due to their efficient conversion of electrical energy into heat and their ability to control temperature.
Cartridge Heating Usage Areas
Cartridge heaters have a wide range of applications and are used in many industrial and domestic settings. Here are some common areas where cartridge heaters are widely used:
Home Heating and Cooling: They are used in home heating systems such as electric heaters, electric stoves, heating fans, and under-carpet heaters.
Kitchen Appliances: Used in kitchen equipment such as ovens, stoves, grills, toasters, coffee makers, and microwave ovens.
Water Heating: Employed in water heaters, dishwashers, washing machines, and hot water tanks.
Industrial Heating: Found in industrial furnaces, dryers, heating tanks, industrial baths, and process heating systems.
Medical Applications: Utilized in medical devices and equipment, sterilization equipment, and laboratory devices.
Automotive: Can be used in vehicle heating and cooling systems, defrosting systems, and in-vehicle climate control systems.
Agriculture and Livestock: Found in greenhouses, poultry houses, animal breeding facilities, and temperature control systems.
Construction: Used in construction areas such as underfloor heating systems, anti-freeze systems, and industrial heating equipment.
Cartridge heaters are preferred in many fields due to their reliability and ease of use.
Technical Specifications of Cartridge Heating Element
Resistance Value: The electrical resistance of cartridge heaters is typically expressed in ohms. This value is determined based on factors such as the material, size, and design of the heater.
Power: The heat energy provided by cartridge heaters is expressed in watts. This is calculated taking into account the electrical current and voltage across the heater. The power of the heater is determined based on the requirements of the application and the size of the environment to be heated.
Voltage: Cartridge heaters are designed to operate within a specific voltage range. For example, heaters typically used for domestic applications operate within the voltage range of 110V or 220V.
Material: Cartridge heaters are typically made from a nickel-chromium (Ni-Cr) alloy. This alloy is preferred for its ability to withstand high temperatures and long lifespan.
Dimensions: The dimensions of cartridge heaters vary depending on the application and intended use. Dimensions such as length, width, and thickness affect the amount of heat provided by the heater.
Thermal Coefficient: This coefficient indicates how much the resistance of the heater can change with temperature variations. It is important for temperature control and stability.
Protective Coating: Some cartridge heaters may be coated with a special coating to protect against corrosion.
Connection Points: The electrical connections of the heater are important for ease of use and safety. Typically, wires or terminals are present at the ends of the heater.
These characteristics may vary depending on the design, production, and intended use of the cartridge heater. Users should consider these technical specifications when selecting the most suitable cartridge heater for a specific application.