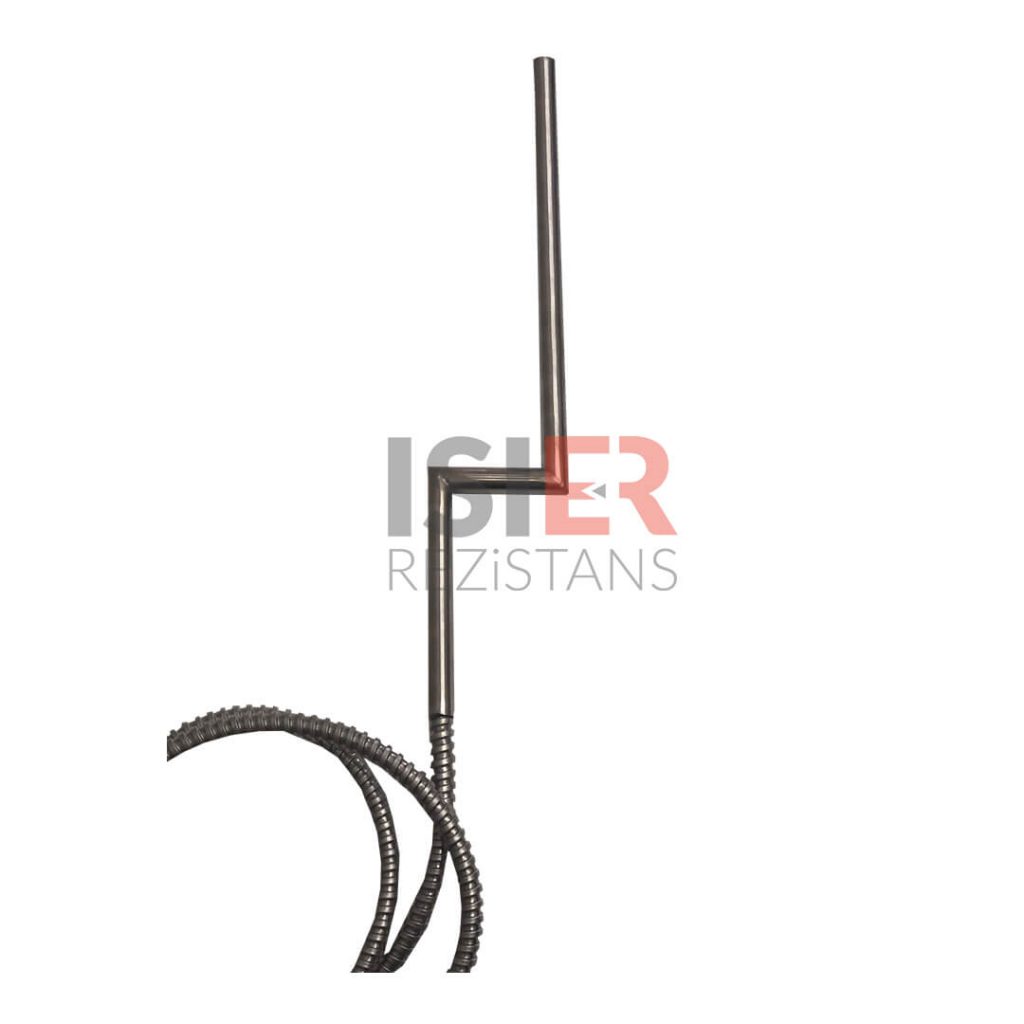
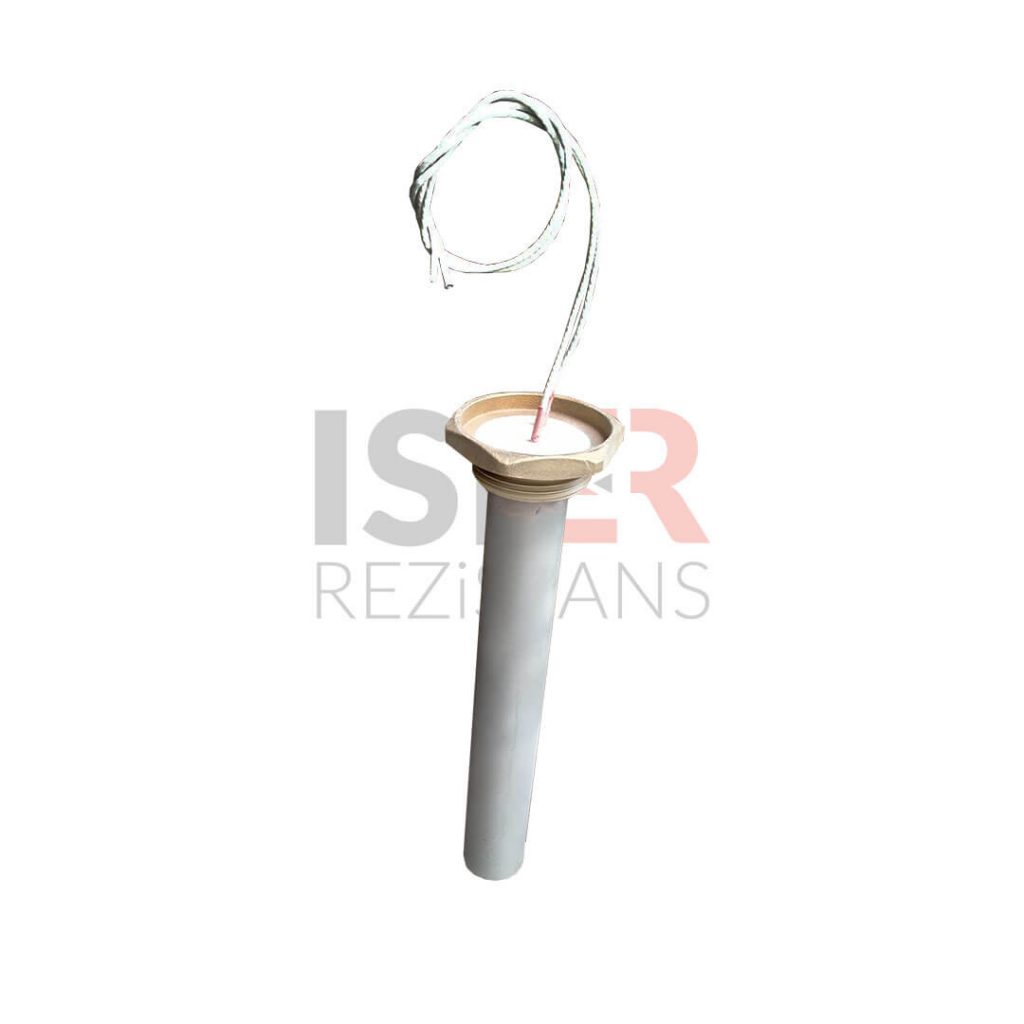
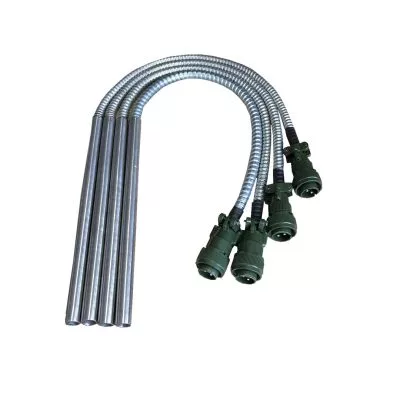
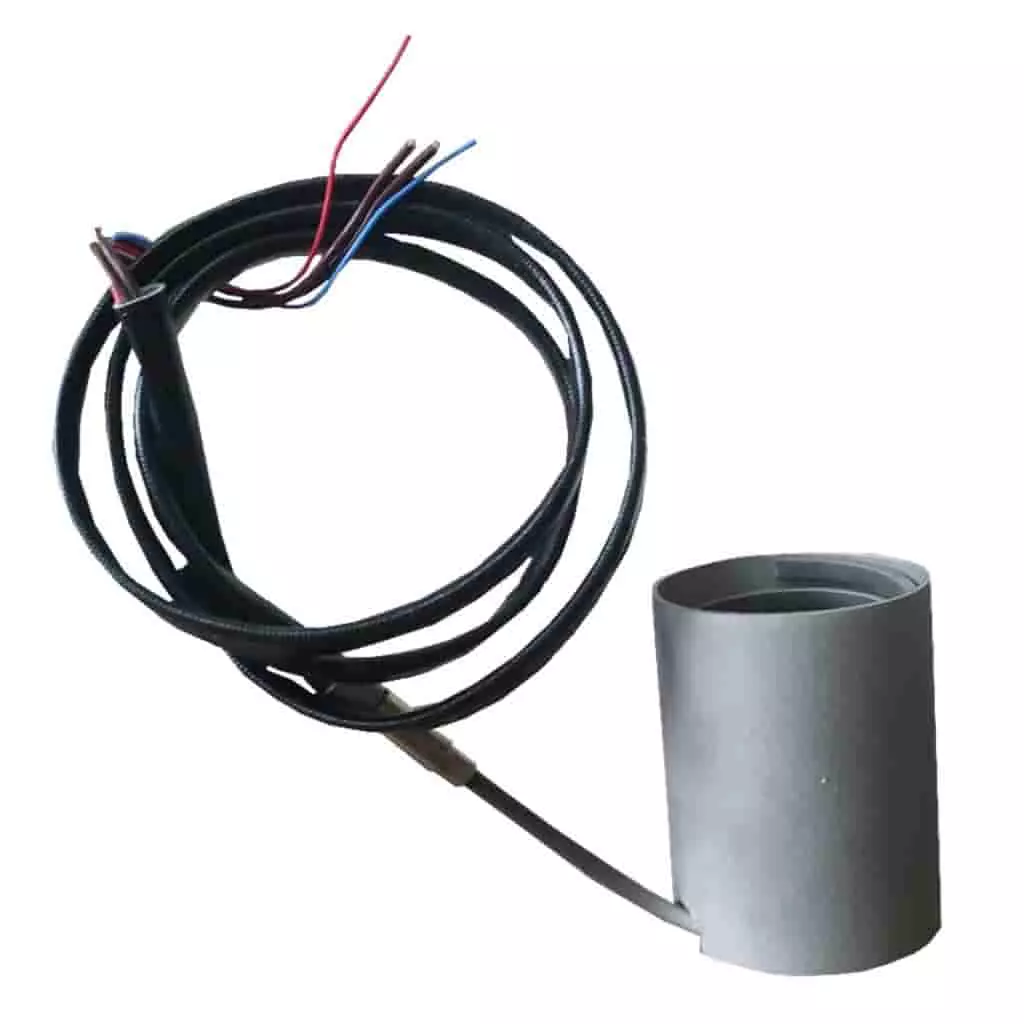
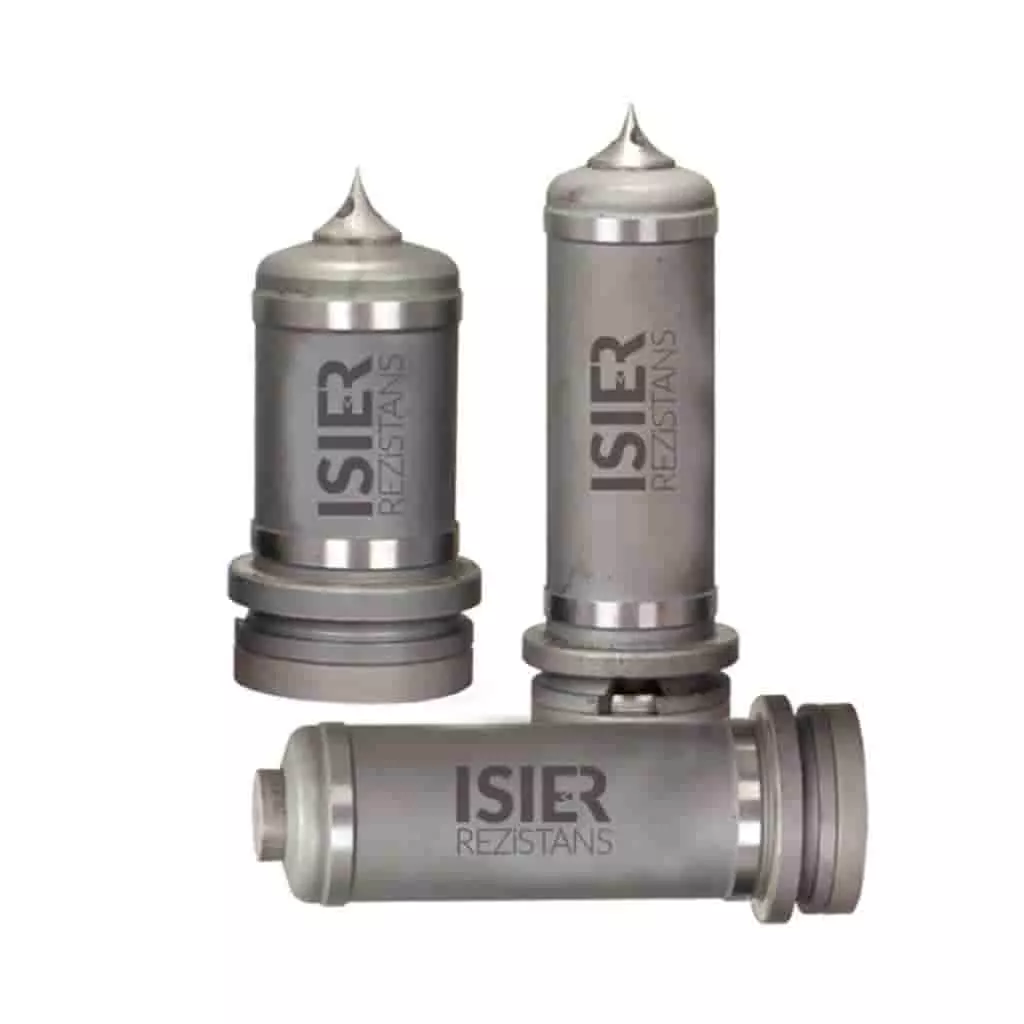
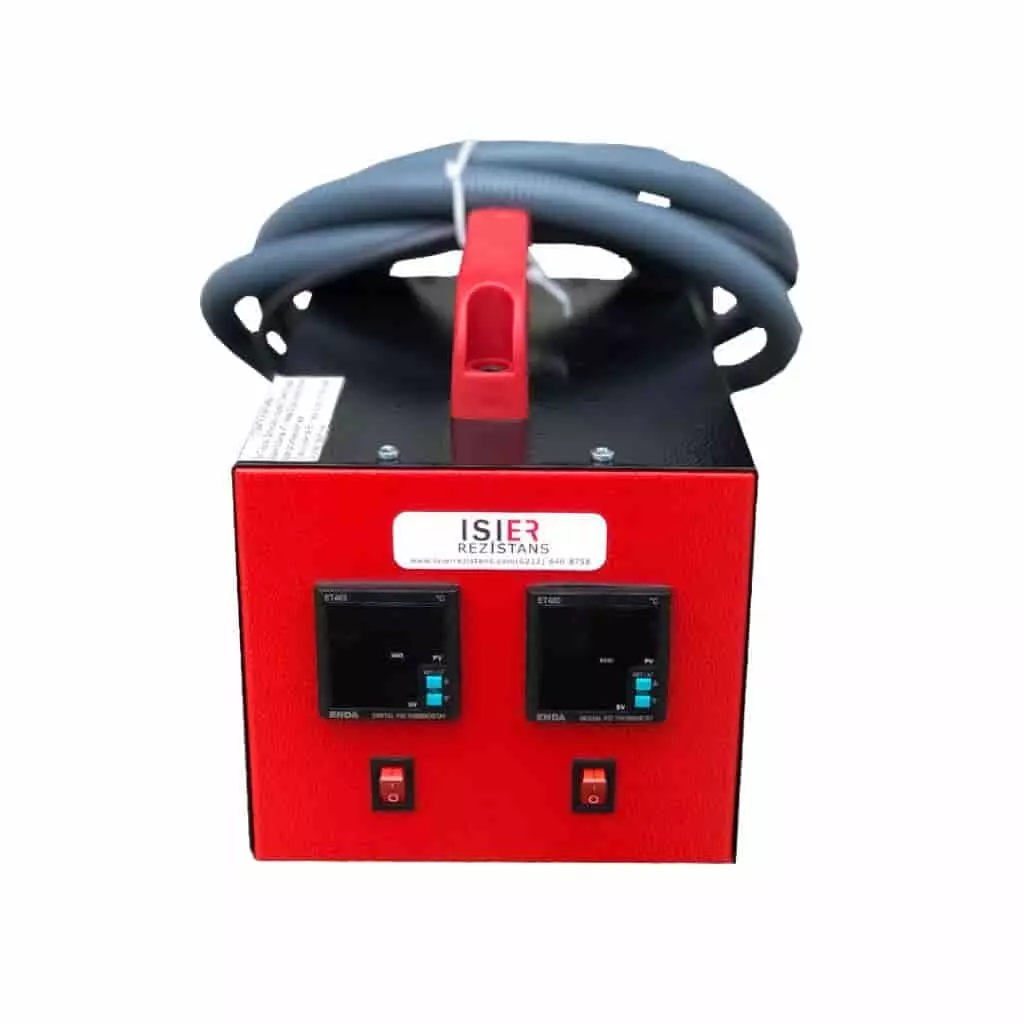
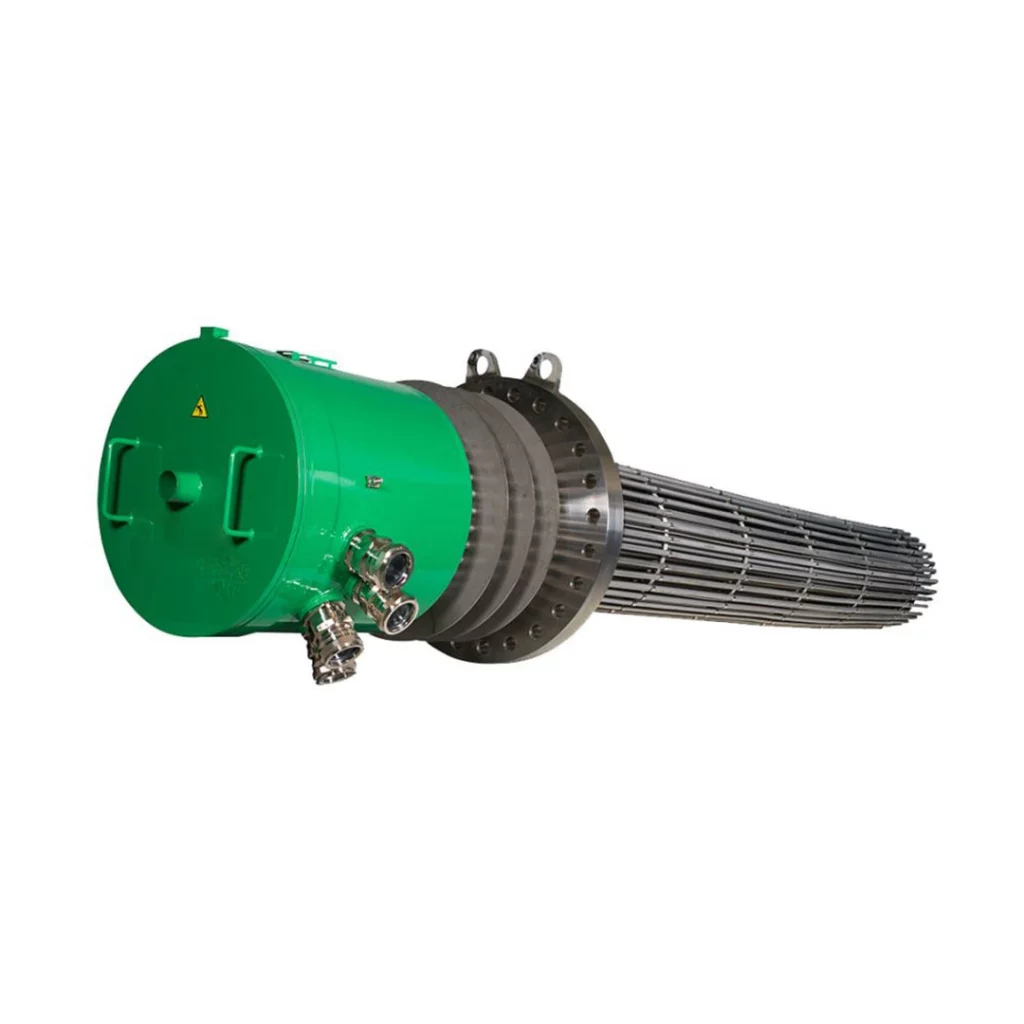
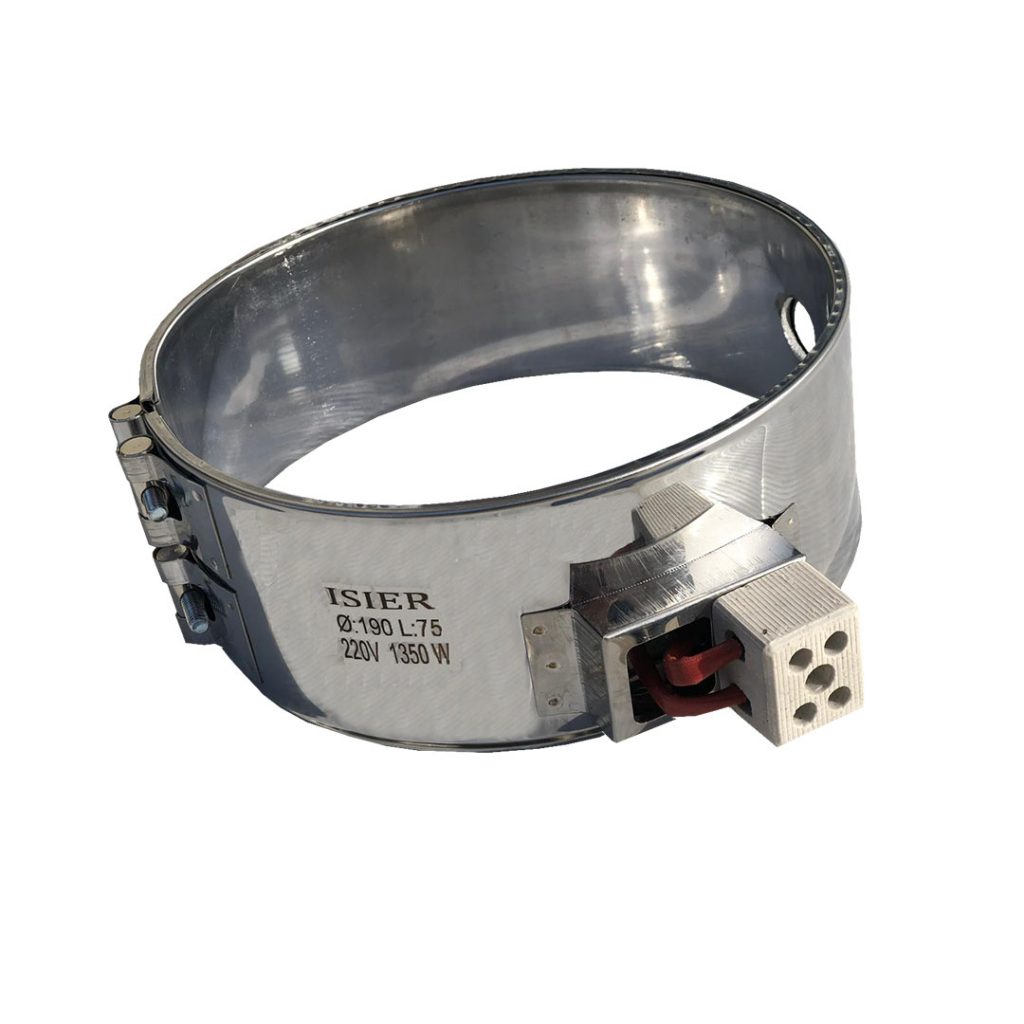
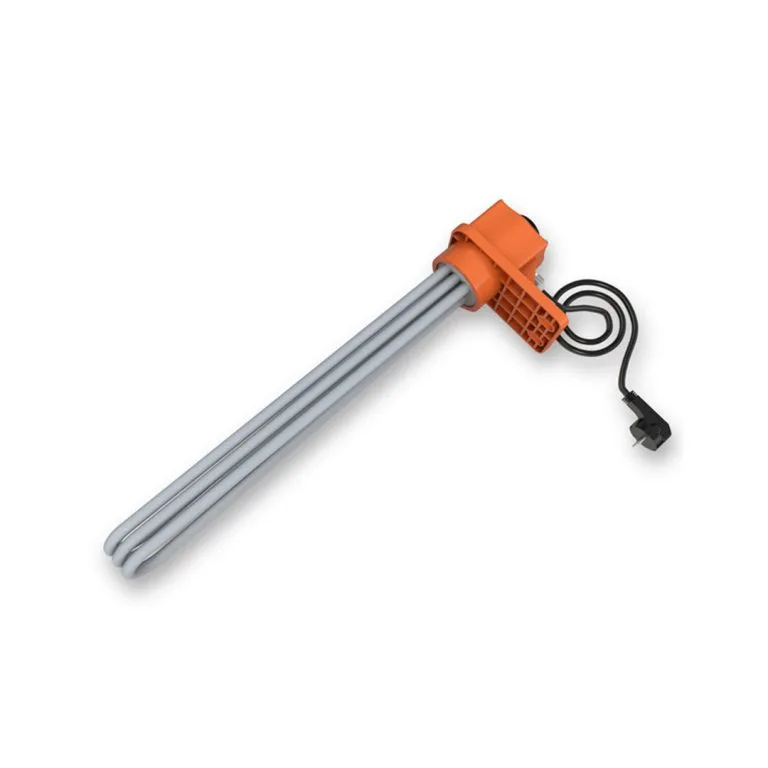
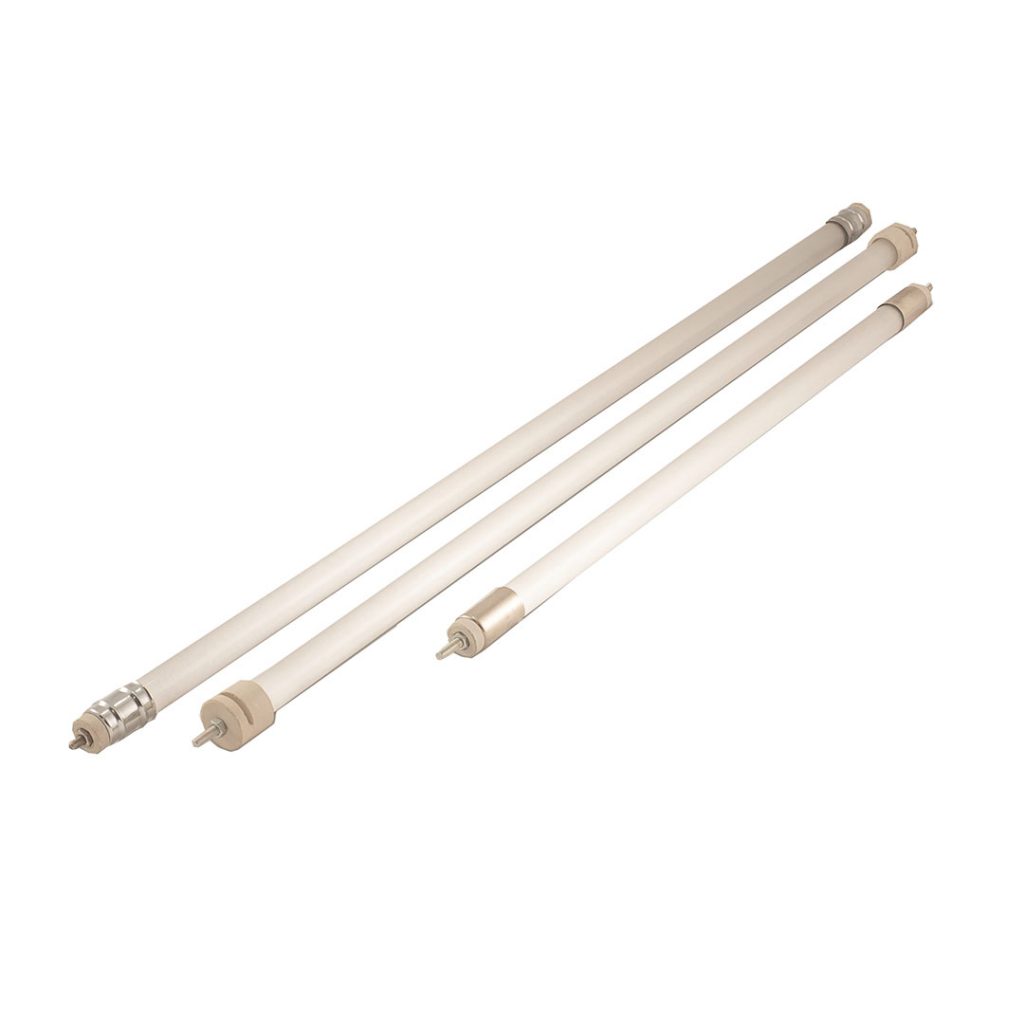
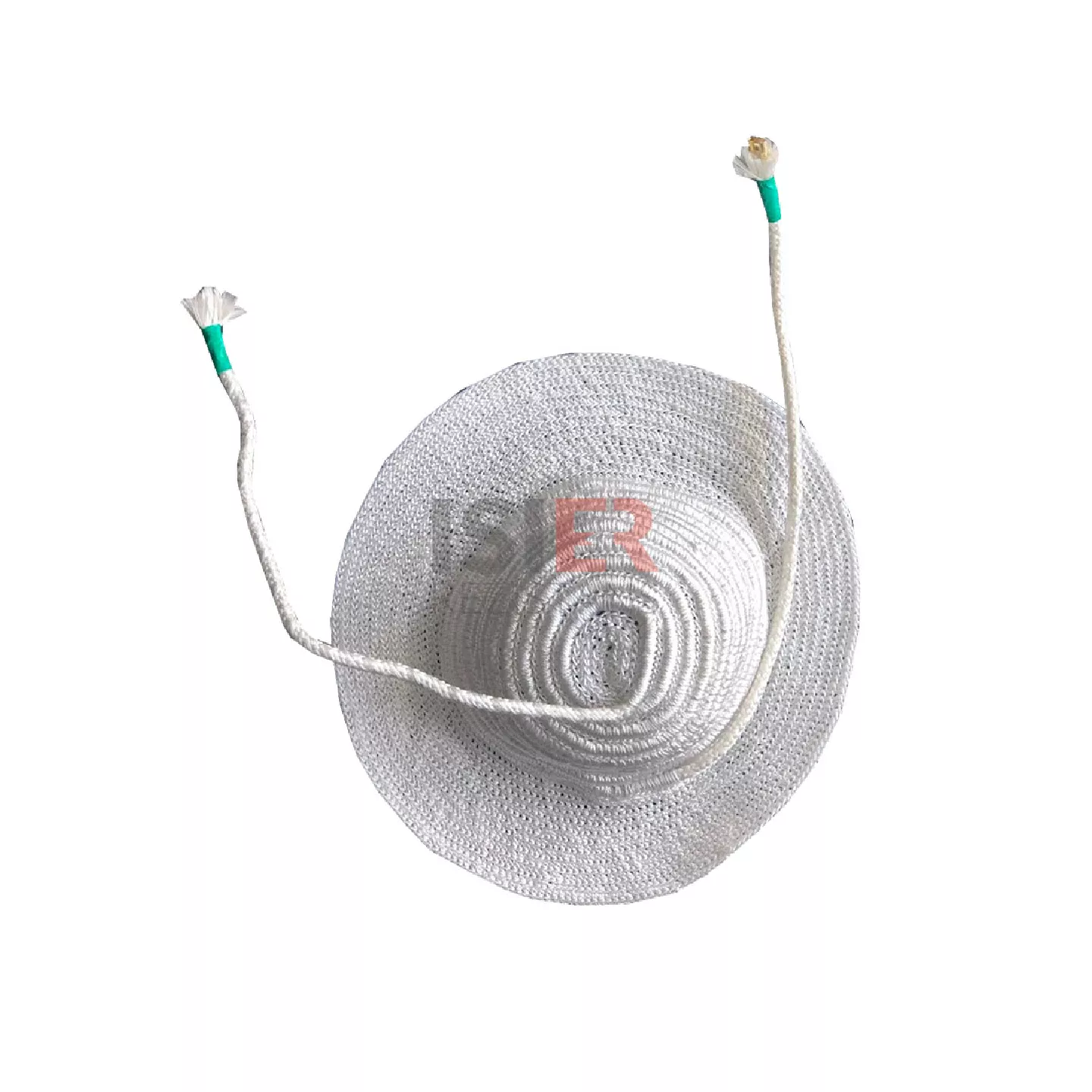
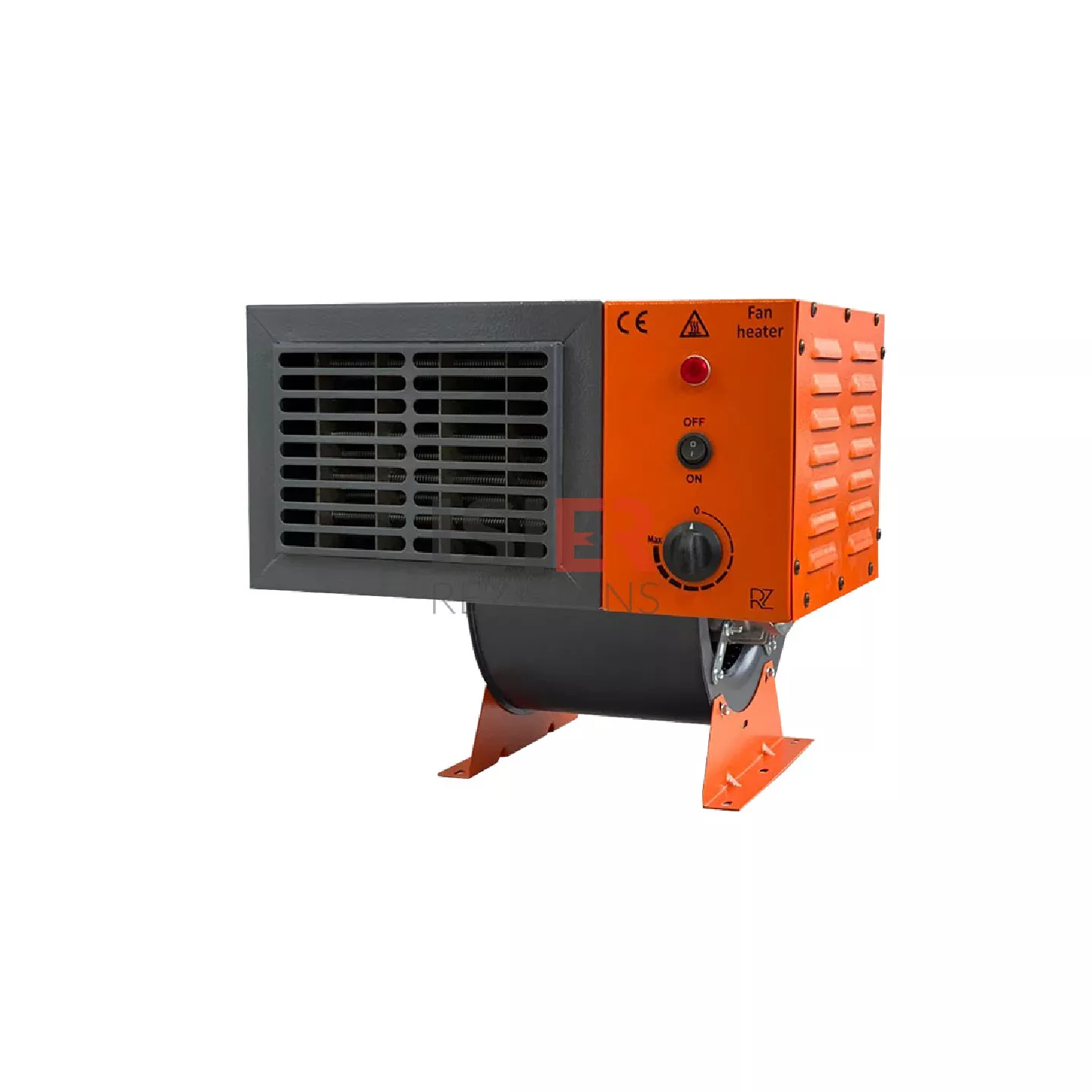
Engineering Heaters
In the engineering sector, heaters are used to provide electrical resistance. They enable the flow of electric current in a circuit against a certain level of resistance. This resistance can be utilized to control or limit the flow of current in an electrical circuit.
Heaters typically generate heat and are therefore commonly used for heating purposes. For instance, in many industrial applications, heaters are used as heating elements. Such applications include furnaces, water heaters, steam generators, industrial drying systems, and many industrial processes.
Additionally, in electronic circuits, heaters can be used for signal processing, filtering, voltage reduction, current limiting, and other electrical functions. They serve as essential components to ensure the proper operation of electrical circuits.

Our Products
Your Solution Partner for All Your Resistance Needs
The Importance of Heating in the Engineering Sector
In the engineering sector, heaters play a significant role in various fields and are utilized in a multitude of applications. Here are some important aspects of heaters in engineering:
Heating Applications: When used to generate heat, heaters are employed in many industrial and residential heating applications such as industrial furnaces, stoves, water heaters, steam generators, plastic extrusion machines, etc. In such applications, it is crucial to generate a stable and controllable heat within specific temperature ranges.
Control Element in Electrical Circuits: In electrical circuits, heaters serve various functions including limiting current, reducing voltage, and providing connections between circuits. In electronic devices and circuits, they ensure proper functioning by providing appropriate resistance levels.
Sensors and Measurement Devices: Heaters can be fundamental components of sensors used to measure physical variables such as temperature, pressure, light, humidity, etc. For example, thermistors are a type of resistance sensor used for temperature measurement.
In Electrical Power Distribution: High-power heaters are utilized in power distribution and control within electrical power systems. For instance, they are used in high-voltage lines to control power factor and regulate current.
In Electric Motors and Devices: Heaters used in starting and control circuits of electric motors and other devices ensure their efficient and safe operation.
In addition to these applications, in the fields of electrical and electronic engineering, heaters are regarded as significant components in terms of circuit design, system integration, and efficiency. Therefore, heaters play diverse and crucial roles in the engineering sector.
Technical Specifications of Heaters Used in the Engineering Sector
The technical specifications of heaters used in the engineering sector can vary depending on their intended purpose and application requirements. However, generally, the following technical specifications are taken into consideration:
Resistance Value: A heater must have a specific resistance value as it is used to limit or control electric current. This value is expressed in ohms.
Tolerance: Tolerance is the maximum allowable deviation between the nominal (specified) resistance of the heater and its actual measured value. Tolerance is usually expressed as a percentage.
Power Rating: The ability of a heater to withstand a certain power level. It is related to the current passing through the heater and the resistance of the heater. Power rating is typically expressed in watts.
Temperature Coefficient: The rate of change of resistance with respect to temperature. It is particularly important in applications sensitive to temperature variations.
Maximum Operating Temperature: The maximum temperature at which a heater can safely operate. This feature is important to prevent overheating and ensure safe operation of the heater.
Material: Heaters can be made from various materials such as metal film, carbon film, wire wound, etc. Each material has its advantages and disadvantages and may be more suitable for specific applications.
Size and Mounting Type: The physical dimensions and mounting type of a heater should be suitable for a specific application. Different mounting types such as surface mount or through-hole mount may be available.
Frequency Response: How a heater responds within a specific frequency range, particularly important in high-frequency applications.
These specifications should be considered based on how the heater will be used in a particular application and its performance requirements. Selecting the appropriate heater ensures the efficient and safe operation of circuits.
Which heaters are used in the engineering sector?
Heaters Made of Carbon: Carbon film heaters are commonly used due to their low cost and wide range of resistances available. The resistance of the carbon film is shaped to the desired value.
Metal Film Heaters: Metal film heaters provide high accuracy and stability. Metal film has a higher temperature tolerance and lower temperature coefficient.
Wire Wound Heaters: Wire wound heaters are typically used in high-power applications. Their coil-shaped structure can distribute higher power values and withstand higher temperatures.
Film Coated Heaters: These heaters are made by coating ceramic substrates with metal film or carbon film. They are preferred in high-frequency applications and places requiring high precision.
SMD (Surface Mount) Heaters: SMD heaters are designed to be compatible with surface mount technology. Due to their small size and lightweight construction, these heaters are commonly used in electronic devices.
Thermal Heaters: Thermal heaters are used for temperature measurement and control. They come in different types such as thermistors and thermocouples. They are widely used for sensing and controlling temperature in heating and cooling systems.
Resistance Burners: Resistance burners used in high-power applications, particularly in industrial heating systems and other applications requiring high power.
These are some common types of heaters used in the engineering sector. Different types of heaters are preferred depending on application requirements and design criteria.