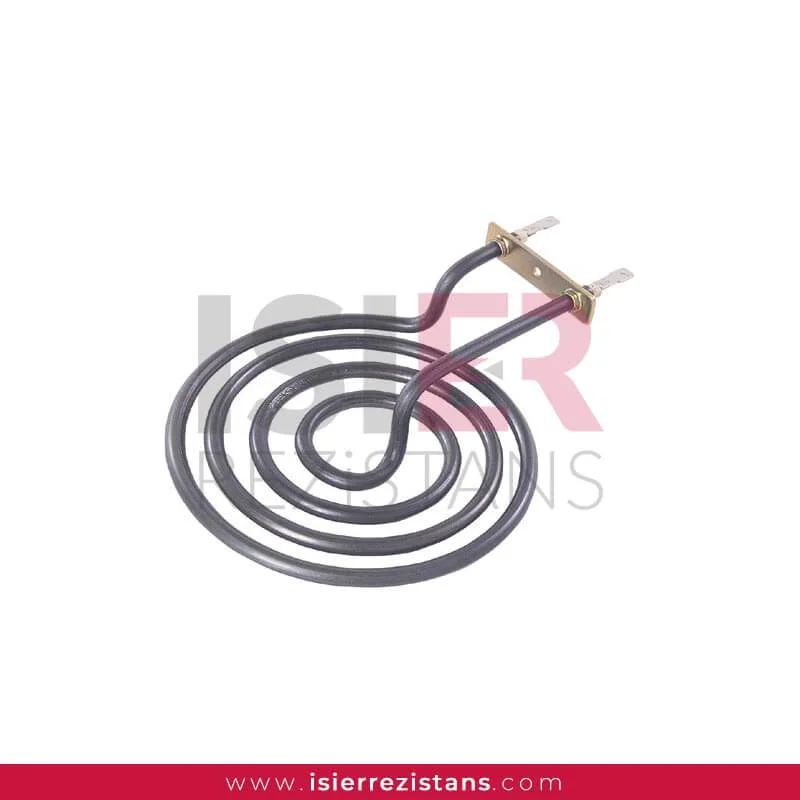
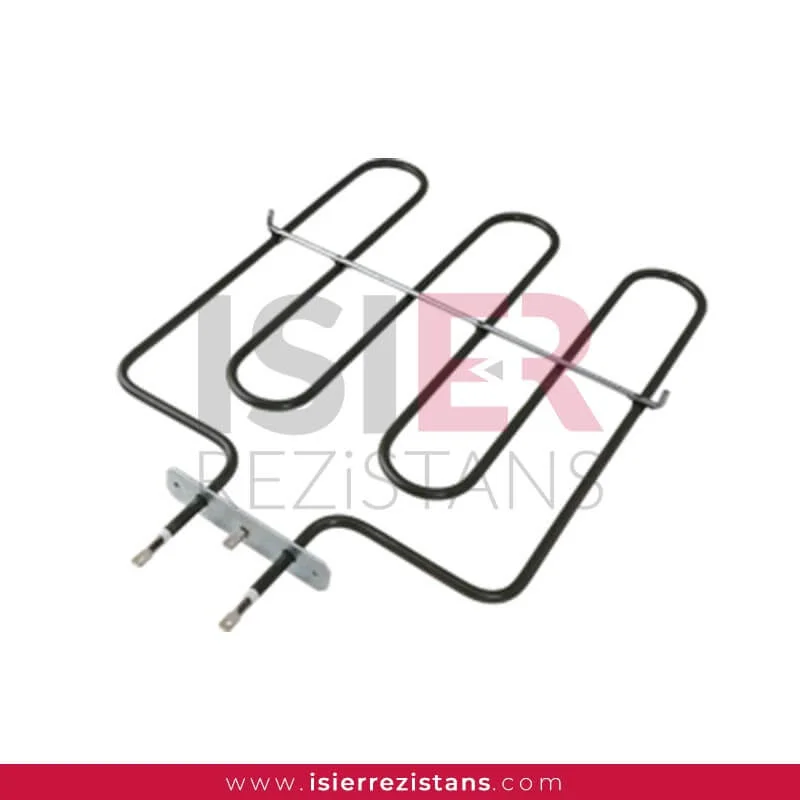
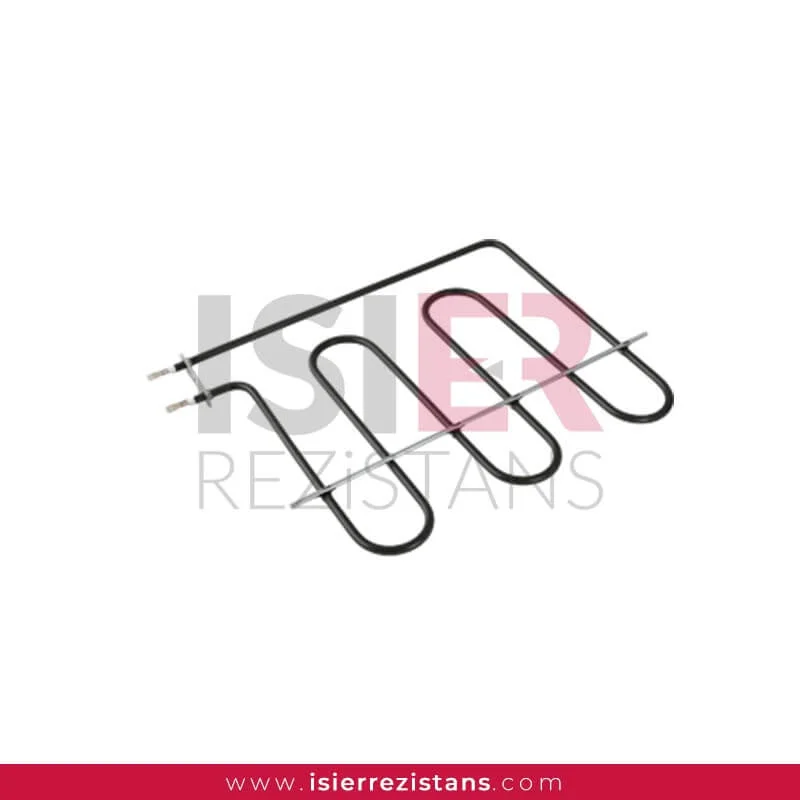
Oven Heaters
Ovens are indispensable appliances with a wide range of applications in our homes or industrial kitchens. Heater elements, which are important components for the effective operation of these ovens and for achieving the desired cooking temperature, are one of the determining factors of cooking performance. In this article, we will explore what heater elements are, how they work, and why they are preferred by oven users.
Working Principle
Heater elements operate based on the principle of resistance (heater). When an electric current passes through the heater, heating occurs due to the resistance of the heater. This heating heats the air inside the oven or the oven walls, allowing the environment to reach the desired temperature level.
Why Choose Oven Heaters?
Fast Heating and Cooking: Heater elements heat up quickly, thus reducing cooking times and allowing users to save time.
High Temperature Capacity: Quality heater elements have a high temperature capacity, enabling a wide range of dishes to be cooked in the oven.
Longevity and Durability: Heater elements made from stainless steel or other durable materials are long-lasting and maintain their performance even with regular use.
Easy Installation and Maintenance: Heater elements are generally easy to install and maintain, allowing users to use their ovens comfortably.
Compatibility with Different Oven Models: There are many different oven models available on the market. Various types and designs of heater elements accommodate different oven models.
Energy Efficiency: High-quality heater elements provide energy efficiency and optimize electricity consumption.
Advanced Cooking Control: Some heater elements may be equipped with temperature sensors and control systems, providing users with precise cooking control.
In conclusion, heater elements are essential components that form the fundamental operating principles of ovens and are indispensable for an effective cooking experience. By selecting quality and suitable heater elements, users can achieve both fast and delicious cooking results.
Oven Heaters Technical Specifications
Heater elements are heating elements found inside ovens, and they typically vary in technical specifications depending on factors such as the material used, power, voltage, resistance value, and physical characteristics. Here is more detailed information about the technical specifications of heater elements:
Material: Heater elements are generally made from heat-resistant materials. Stainless steel, nickel-chromium alloys, or ceramic materials are commonly preferred. Stainless steel provides durability and resistance to corrosion. Nickel-chromium alloys are resistant to high temperatures, and ceramic materials are particularly preferred for ceramic heaters.
Power (Watt): The power of heater elements is usually expressed in watts. The power value determines how much the heater element heats up and is typically selected based on the size of the oven and its intended use. For example, power values between 1500W and 3000W can be used for household ovens.
Voltage: Heater elements typically operate at the standard household electricity voltage of 220V or 230V. However, different voltages can also be used for industrial ovens or special applications.
Resistance Value (Ohm): The resistance value of the heater element measures its resistance to electrical current and is usually expressed in ohms. The resistance value of heater elements can vary depending on the material and design.
Size and Physical Characteristics: Heater elements can come in various sizes and shapes depending on the design and model of the oven. Various designs such as spiral elements, flat elements, or tube-shaped elements can be found. Physical characteristics are important for easy integration into the oven.
Temperature Capacity: High-quality heater elements typically have a high temperature capacity, allowing the oven to reliably operate at high temperatures.
Durability and Lifespan: Heater elements made from stainless steel or special alloys provide durability and a long lifespan. These features help maintain performance during regular use.
Ease of Installation: The installation of heater elements should be easy to minimize any difficulties users may encounter when setting up their ovens. Standard connection types and installation instructions provide this convenience.
Additional Features: Some heater elements may be equipped with temperature sensors, thermostats, or other control mechanisms. These features enable more precise cooking control and energy efficiency.
Oven Heaters Usage Areas
Heater elements are heating elements widely preferred in various fields within a broad spectrum of usage. Here are the common areas where heater elements are extensively used:
Home Ovens:
Home ovens utilize heater elements to heat the air inside or the oven surface, enabling the cooking of food. These ovens are typically used in household kitchens, and heater elements are integrated into various home oven models.
Industrial Ovens:
Industrial ovens are used in large-scale manufacturing facilities, industrial establishments, or laboratories. Heater elements heat the interior of industrial ovens to cook, dry, or process materials.
Pizza Ovens:
Restaurants or pizzerias use specially designed heater elements in pizza ovens. These elements enable pizza ovens to operate at high temperatures, allowing pizza dough to cook quickly and efficiently.
Oven Ranges:
Heater elements support oven functions in kitchen ranges found in household kitchens. These ranges are used to diversify cooking processes.
Gastronomy and Catering:
Large events, weddings, or catering services require cooking large amounts of food. Heater elements are used in industrial ovens and large kitchen appliances for such applications.
Bread Ovens:
Heater elements are used in bread ovens where bakery products (bread, pastries, etc.) are baked. These ovens are typically equipped with heater elements to ensure bread is baked at the desired temperature and evenly.
Laboratory Ovens:
Laboratory ovens used in scientific and research laboratories operate with heater elements. These ovens are used to process, dry, or test materials at specific temperatures.
Heating and Drying Applications:
Heater elements are commonly used in industrial applications for heating or drying materials. These applications can be found in metal processing, ceramic production, the food industry, and many other fields.
Heater elements play a significant role in various sectors due to their wide range of applications. They provide a reliable heating solution to achieve and maintain desired temperature levels.
In which sectors oven heaters are used
Heater elements are heating elements widely preferred in many areas within a broad spectrum of usage. Here are the common areas where heater elements are extensively used:
Home Ovens: Household ovens use heater elements to heat the air inside or the oven surface, allowing food to be cooked. These ovens are typically used in home kitchens, and heater elements are integrated into various home oven models.
Industrial Ovens: Industrial ovens are used in large-scale manufacturing facilities, industrial establishments, or laboratories. Heater elements heat the interior of industrial ovens to cook, dry, or process materials.
Pizza Ovens: Restaurants or pizzerias use specially designed heater elements in pizza ovens. These elements enable pizza ovens to operate at high temperatures, allowing pizza dough to cook quickly and effectively.
Oven Ranges: Heater elements support oven functions in kitchen ranges found in household kitchens. These ranges are used to diversify cooking processes.
Gastronomy and Catering: Large events, weddings, or catering services require cooking large amounts of food. Heater elements are used in industrial ovens and large kitchen appliances for such applications.
Bread Ovens: Heater elements are used in bread ovens where bakery products (bread, pastries, etc.) are baked. These ovens are typically equipped with heater elements to ensure bread is baked at the desired temperature and evenly.
Laboratory Ovens: Laboratory ovens used in scientific and research laboratories operate with heater elements. These ovens are used to process, dry, or test materials at specific temperatures.
Heating and Drying Applications: Heater elements are commonly used in industrial applications for heating or drying materials. These applications can be found in metal processing, ceramic production, the food industry, and many other fields.
Heater elements play a significant role in various sectors due to their wide range of applications. They provide a reliable heating solution to achieve and maintain desired temperature levels.