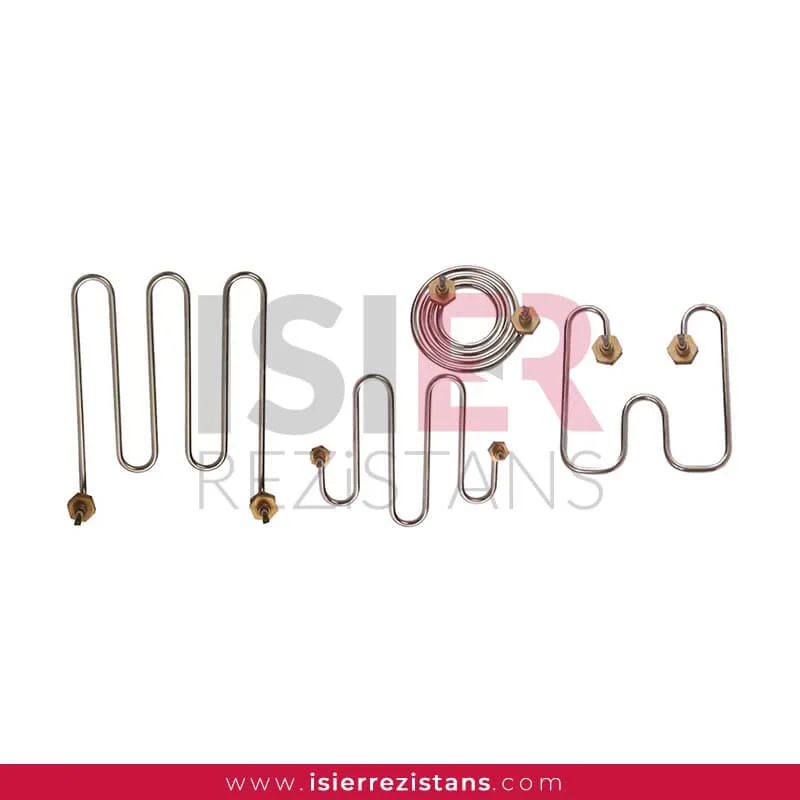
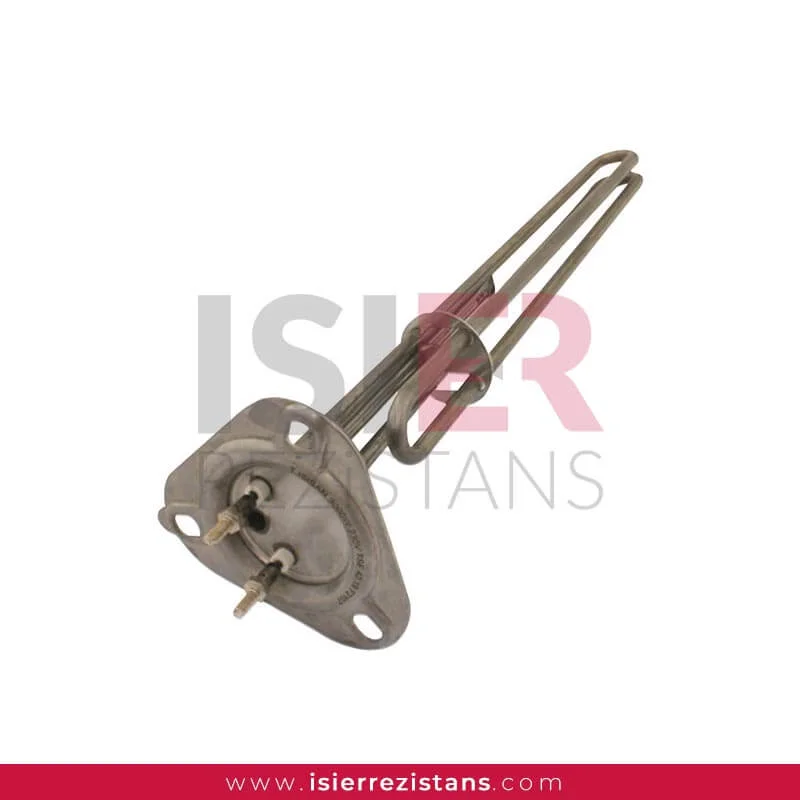
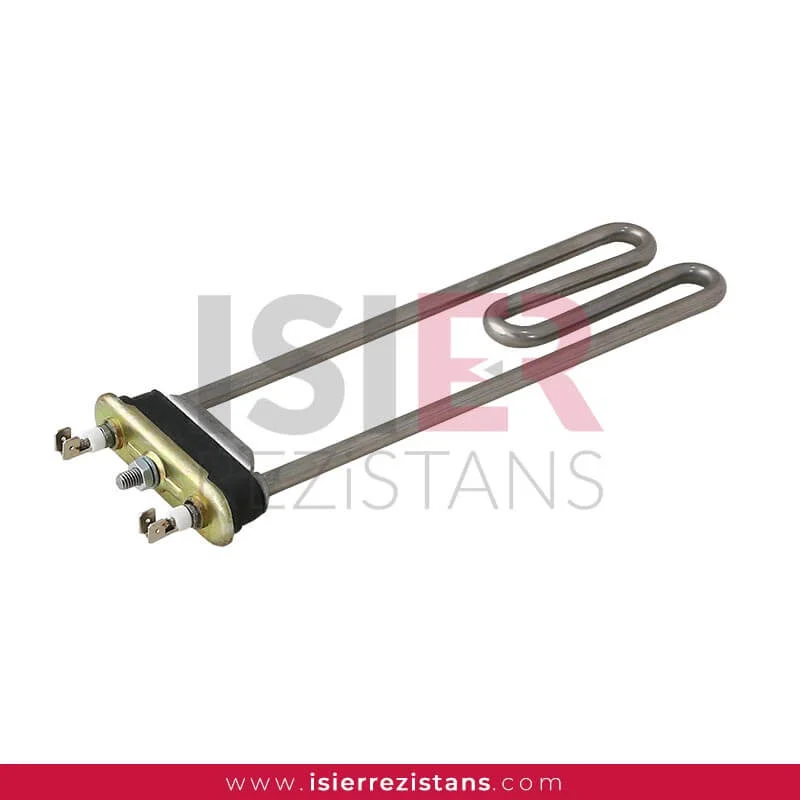
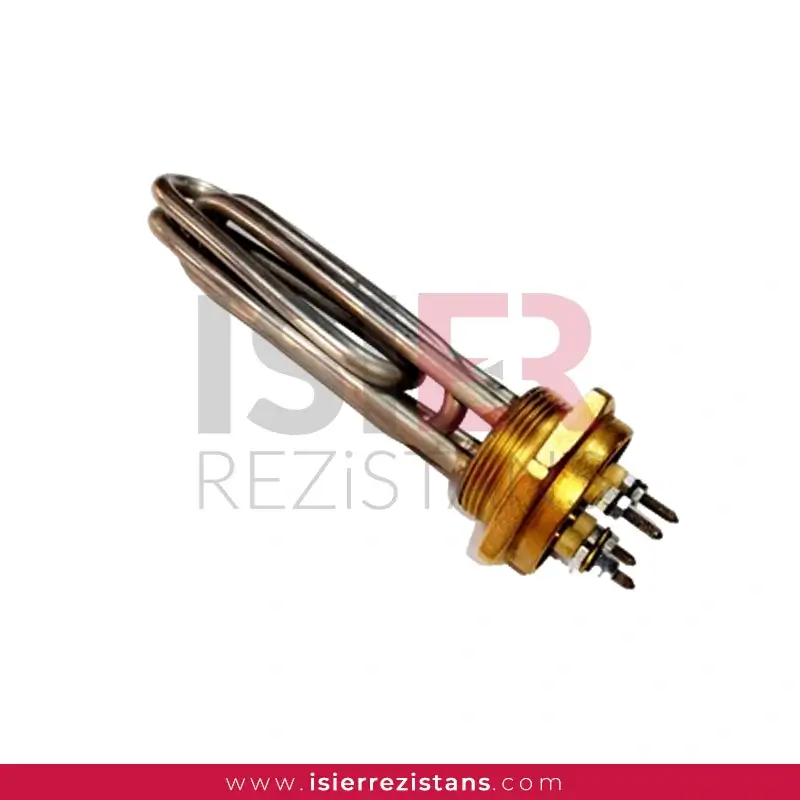
Tubular Heating Elements
Tubular Heating Elements that are produced in pipe form and be given different forms. Tubular Heating Elements, which have different qualities depending on the amount of resistance;is the most commonly used type of resistance in industrial areas. This type of resistance, which a wide range of uses, serves by converting electrical resistance to very high temperatures. This type of resistance includes liquid heaters and outdoor heaters.
Elements which have a wide range of uses from kitchen equipment to industrial vehicles, have become frequently used industrial equipment with their robust structure.
Tubular Heating Types
Your Solution Partner for All Your Heater Needs
Technical Information
Tubular Heating Elements wide range of uses in industrial, commercial and scientific fields. Tubular Heating Elements
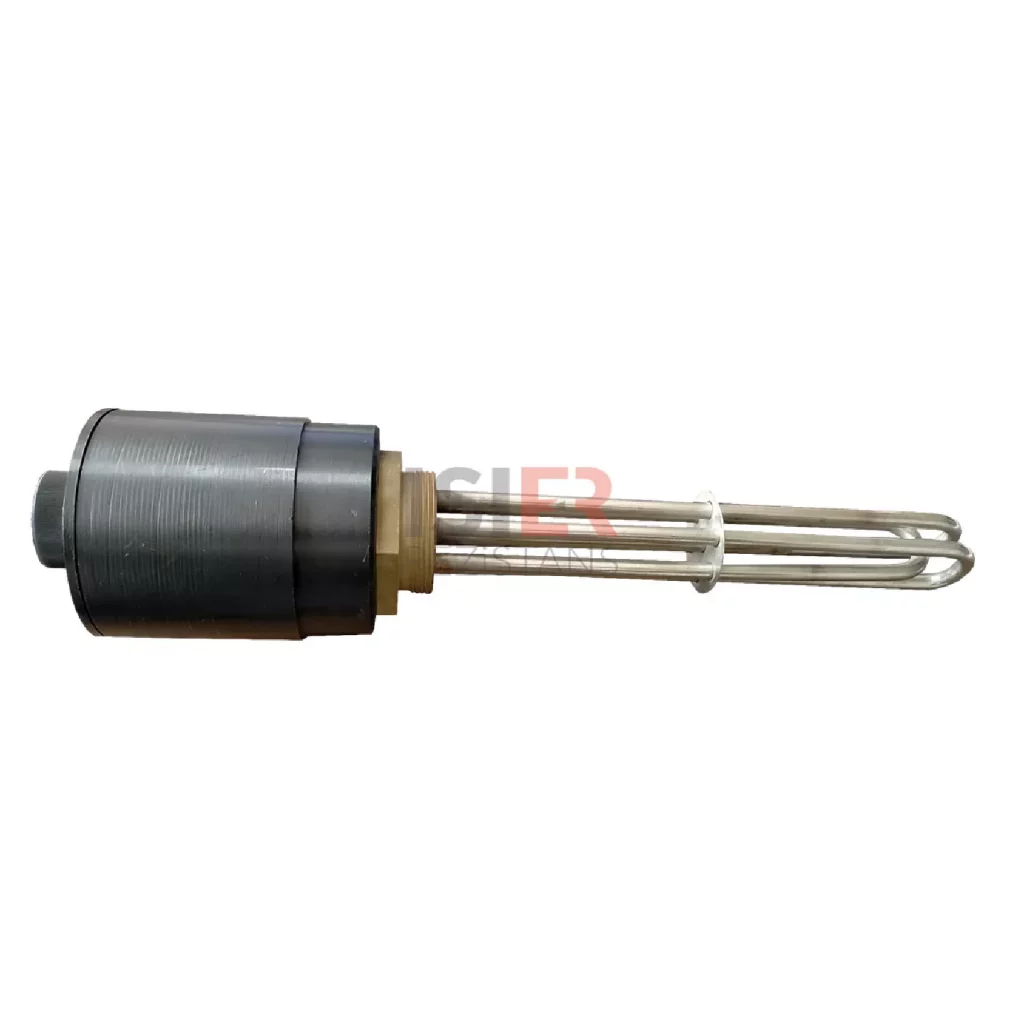
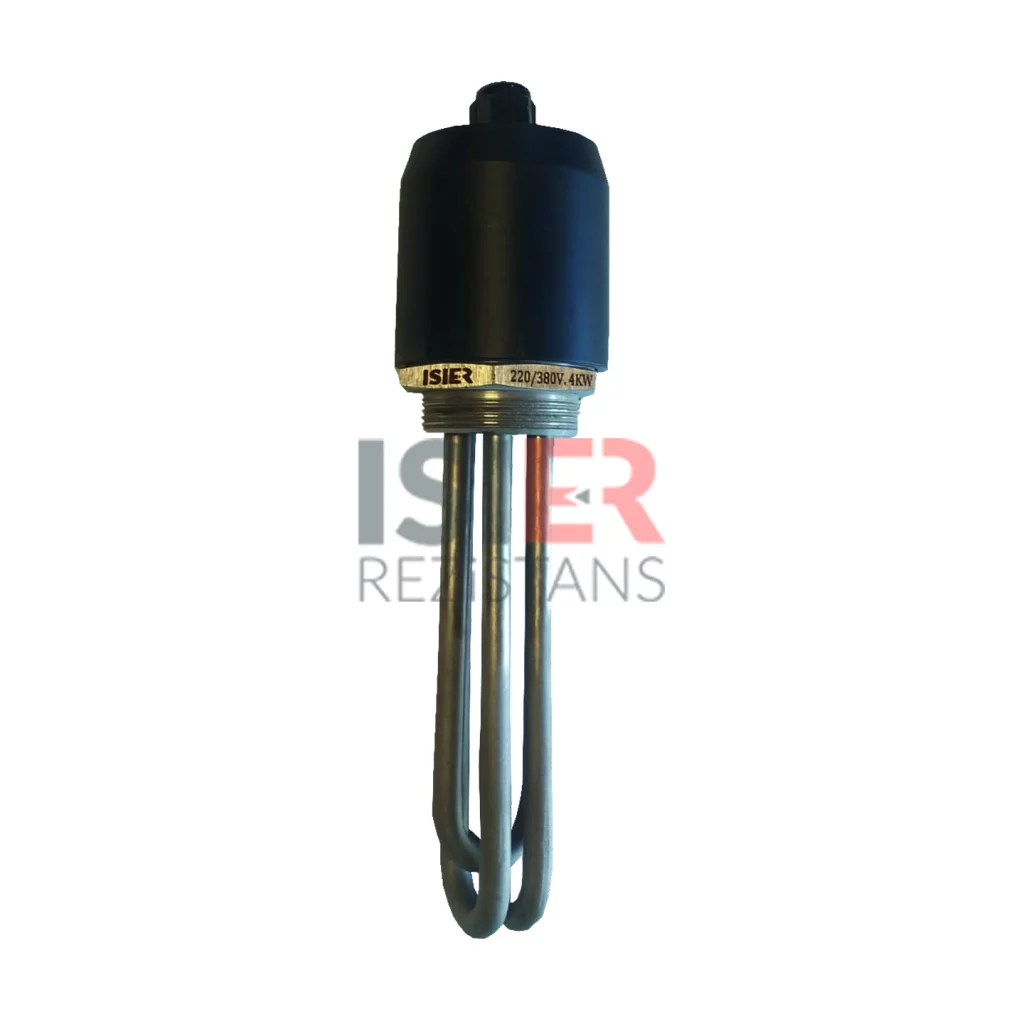
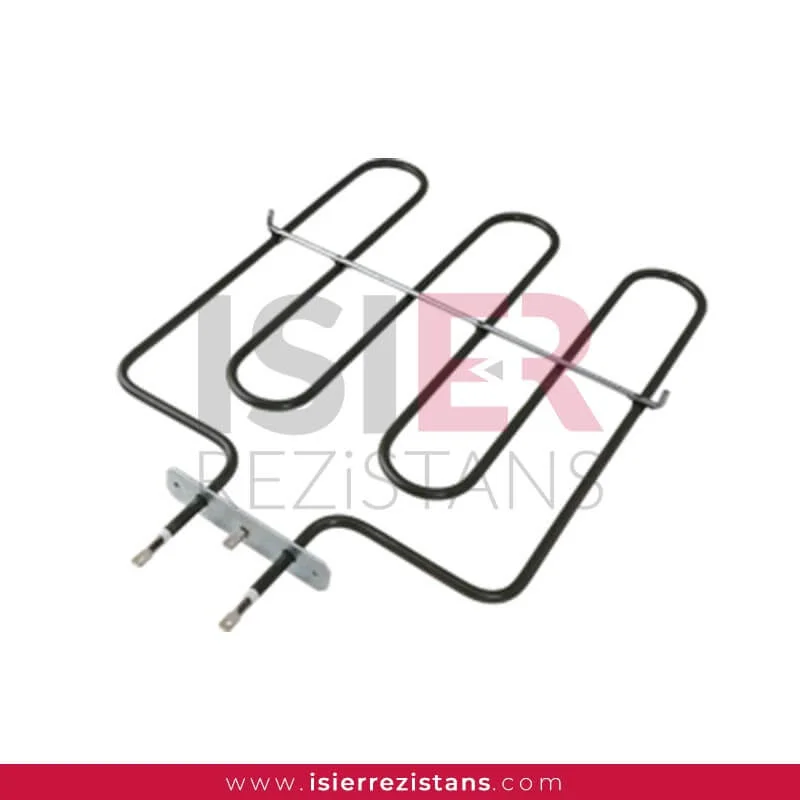
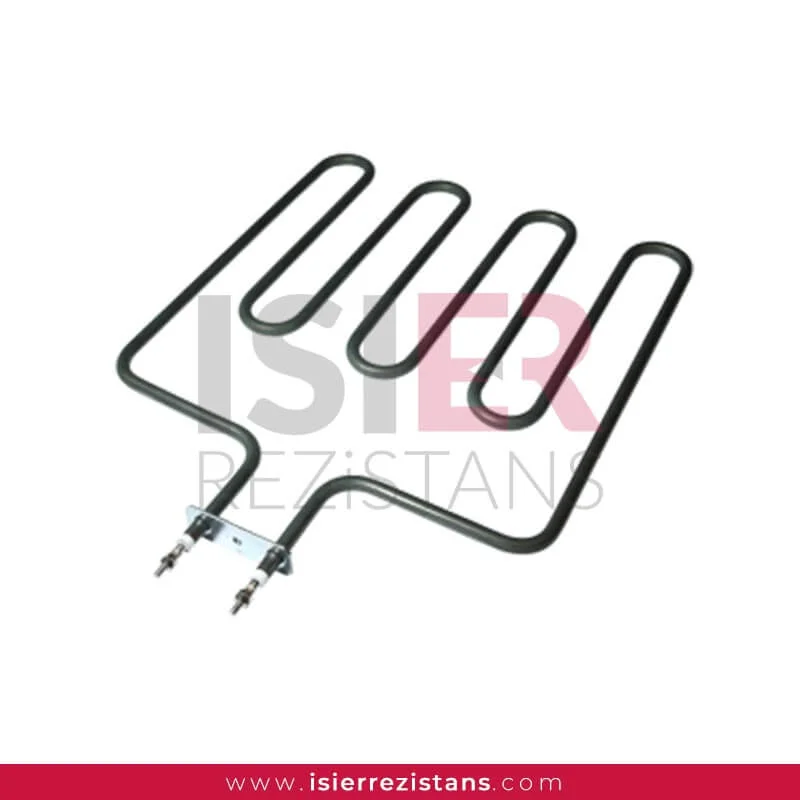
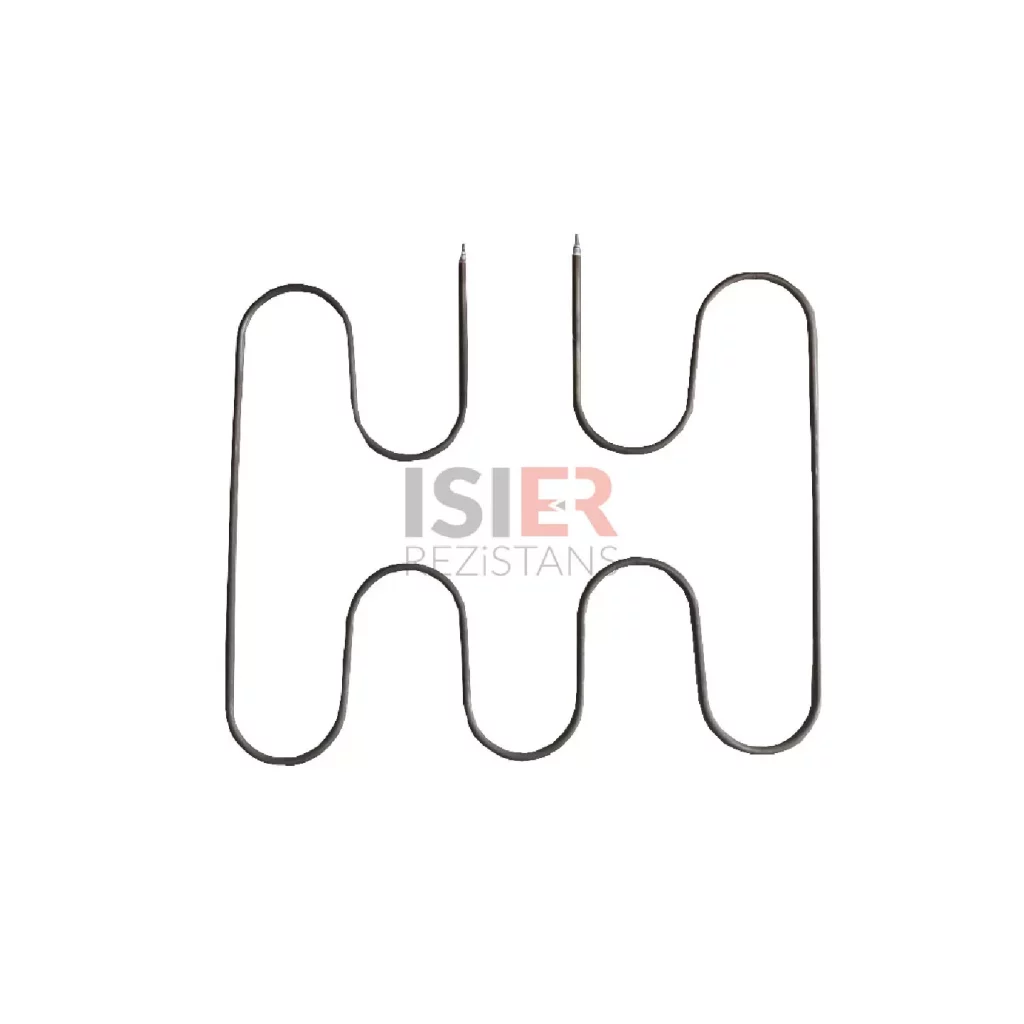
consist of parts such metal sheaths and connectors. Thanks to the easy forming of resistors, welding can be made and soldered to every metal surface. In this respect,be easily integrated into the systems. Pipe resistors be produced as flat and curved as desired as flat and curved as desired with sleeve, record, flanch, serpentine, aluminum coat,in the size and power determined according to the place. For example, if you want to know what you’re going to Flat bar,U type, type M are the most common uses.
Tubular Heating Elements
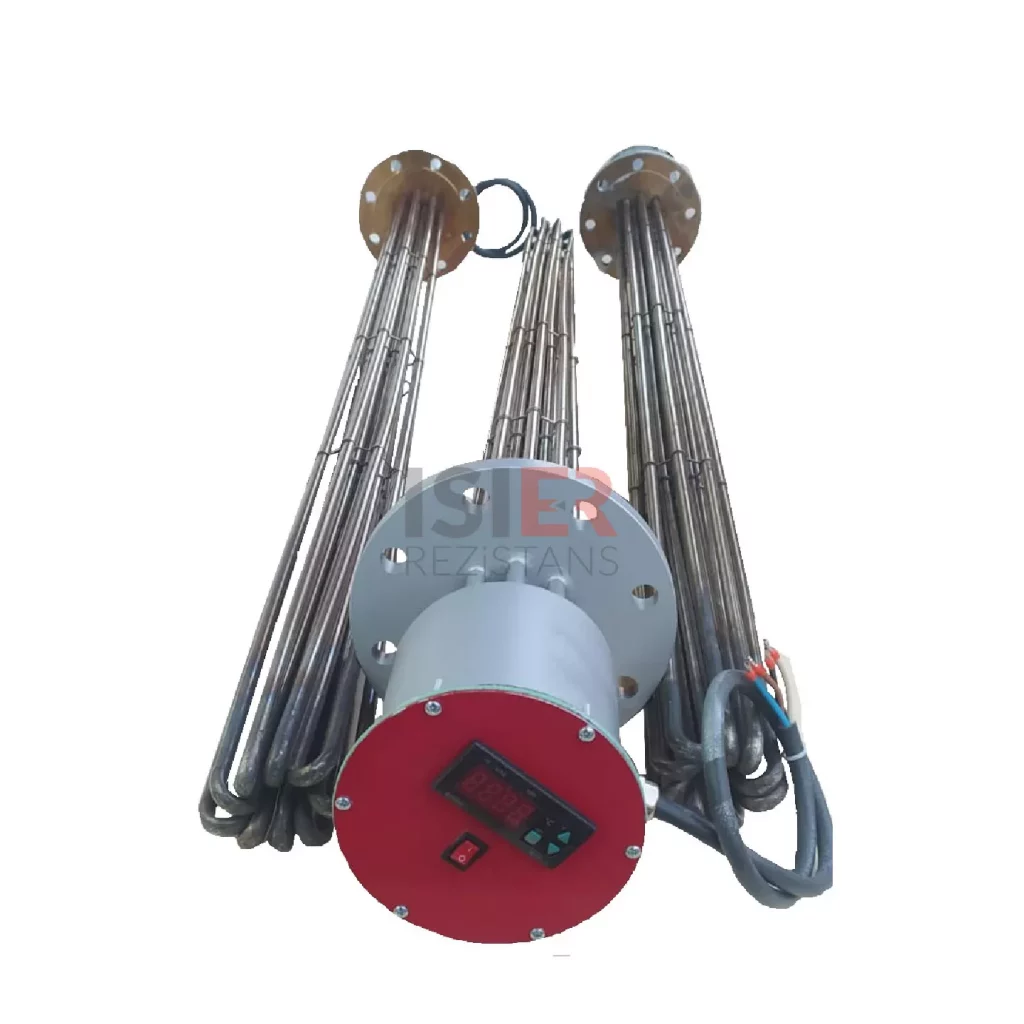
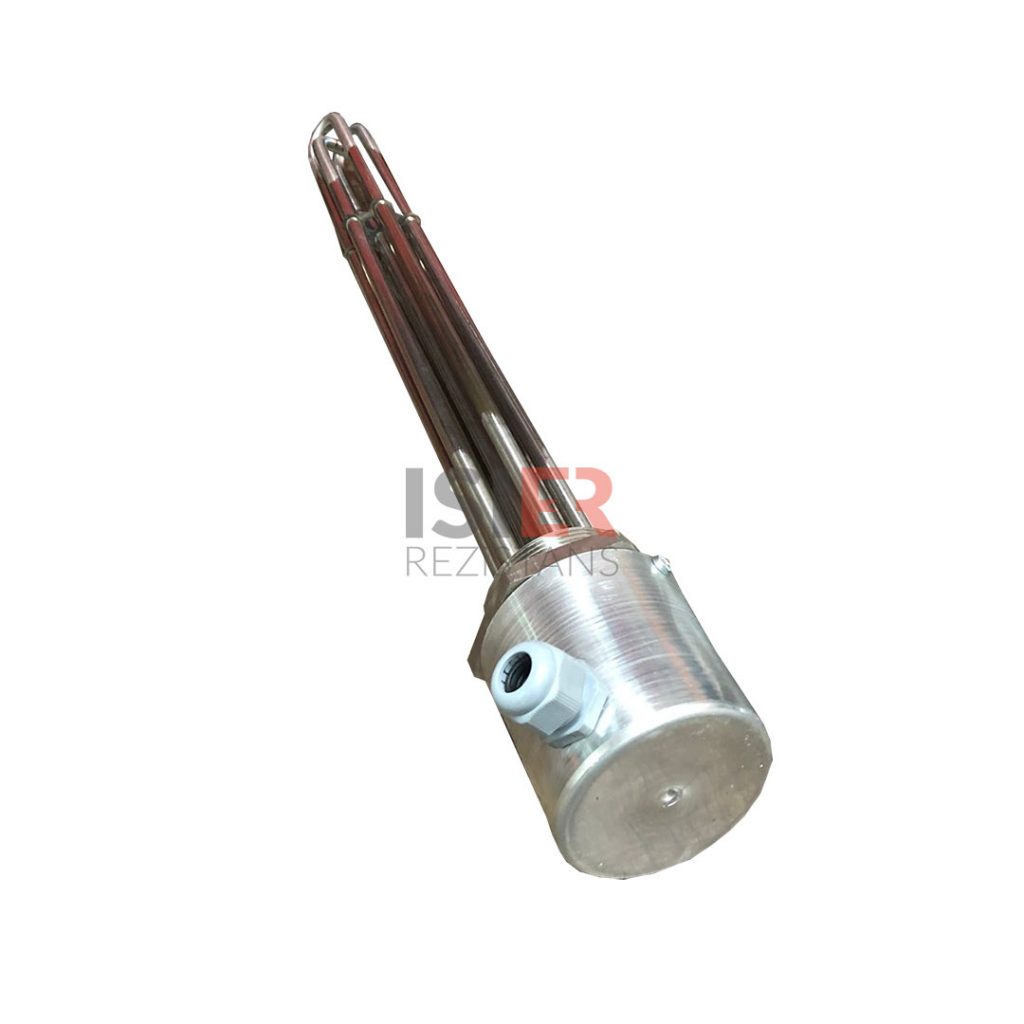
which are also developed as industrial types, are preferred in many different areas for heating water, oil, chemical and corrosive liquids. Industrial pipe resistors are also used for heating molds and different metal materials in industrial industrial furnaces.
What is Tubular Heating Elements ?
Tubular heaters are electromagnetic devices of various dimensions and shapes used to control the flow of fluids passing through tubes. High flow rates of fluids within tubes can lead to energy loss and wastage of resources at sources. Tubular heaters are utilized to regulate this energy loss and provide resistance to reduce the speed of fluid flow.
Tubular heaters can be made of metallic materials such as nickel, tungsten, carbon, or their mixtures. They may possess a specific resistance value, which can be utilized to control the speed of fluid flow. Additionally, tubular heaters can operate within a specific temperature range and have a certain power capacity.
Tubular heaters find applications across various sectors including industry, energy, water supply systems, environment, and are selected based on the required features to control the speed of fluid flow.
Types of Tubular Heaters
Tubular heaters can vary in sizes, shapes, materials, and characteristics, and can be classified into different types based on these attributes. Below are some types of tubular heaters:
Electromagnetic Tubular Heaters: These heaters can be made from metal materials such as nickel, tungsten, carbon, or their mixtures.
Thermistor Tubular Heaters: These heaters rely on the change in resistance with temperature variation.
Radial Tubular Heaters: These heaters can be designed with different dimensions and can provide resistance based on the direction of fluid flow.
Axial Tubular Heaters: These heaters can provide resistance based on the horizontal direction of fluid flow.
Thermostatic Tubular Heaters: These heaters can be used with temperature control systems and can change their resistance when a specific temperature value is reached.
This classification can vary depending on the application, operating conditions, and requirements of tubular heaters, and combinations of different types can also be utilized.
Tubular Heaters Areas of Use
Tubular heaters can be utilized in various applications such as:
HVAC Systems: In heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, tubular heaters can be used to control fluid flow and heat distribution.
Energy Generation: In systems like thermal, hydroelectric, or solar power, tubular heaters can be used to control fluid flow.
Chemical and Petrochemical Industry: In chemical and petrochemical plants, tubular heaters can be used to control fluid flow and heat.
Water and Wastewater Management: In water facilities, tubular heaters can be used to control fluid flow and pressure.
Industrial Processes: In industrial processes, tubular heaters can be used to control fluid flow and temperature.
This is just a subset of the places where tubular heaters can be employed. The design and characteristics of tubular heaters can vary depending on different applications and requirements.
Tubular Heatings Technical Specifications
The technical specifications of tubular heaters may include:
Operating Pressure: The maximum operating pressure is the highest fluid pressure that the tubular heater can withstand.
Operating Temperature: The operating temperature range refers to the minimum and maximum temperatures at which the tubular heater can be used.
Flow Capacity: The maximum amount of fluid that the tubular heater can pass on a daily basis.
Material: The material used for the construction of the tubular heater should be selected based on the application’s conditions and fluid properties.
Dimensions: The dimensions of the tubular heater should be determined based on the pipe sizes, application requirements, and fluid flow.
Connection Types: Tubular heaters can have different connection types, such as rigid, flexible, etc. The connection type should be chosen based on the application’s conditions and fluid properties.
Tubular Heating Elements
Tubular heaters are metal heaters that can be manufactured in different shapes and are commonly used in industrial settings. These heaters, which have properties that vary according to resistance levels, function by converting electrical energy into high temperatures. Among tubular heaters, there are liquid heaters and open heaters. With various application areas ranging from kitchen equipment to industrial machinery, these types of heaters are often preferred in industrial equipment due to their durable structures.
Tubular Heating Technical Data
Tubular heater types are commonly used for heating chemical and corrosive liquids, as well as for heating molds and various metals in industrial furnaces.
These types of heaters can be manufactured in diameters of 6.5 mm, 8.5 mm, 11.5 mm, 14.5 mm, and 16.00 mm, and can be easily produced in any size from 5 mm to 20 mm.
Tubular heaters have a wide range of applications in industrial, commercial, and scientific fields. They consist of parts such as metal casing and connection ends, and can easily take shape, allowing welding or soldering to any metal surface. Therefore, integrating them into systems is quite easy. Tubular heaters can be produced as desired, with sleeves, sheaths, flanges, coils, and aluminum coatings, in straight or curved shapes. For example, straight rods, U-shaped, and M-shaped are the most commonly used shapes.
Tubular heaters developed for industrial use are preferred in many different fields for heating water, oil, chemicals, and corrosive liquids. Industrial tubular heaters are also used for heating molds and various metal materials in furnaces found in industrial environments.
In addition to round tubular heater types, flat-shaped heaters of varying sizes can also be produced. Common applications of these heaters include railway switch heating, oil heaters in industrial fryers, and dry air heaters in some special ovens.
Tubular heater models are widely used in various fields such as the plastic industry, packaging industry, woodworking industry, construction industry equipment, household appliances, foundry industry, high vacuum applications, and laboratory equipment.
Tubular Heatings Types
Tubular heaters can come in various sizes, shapes, materials, and specifications, leading to classification into different types based on these attributes. Here are some types of tubular heaters:
Electromagnetic Tubular Heaters: These types of heaters, made from metal materials such as nickel, tungsten, carbon, or their mixtures, convert electrical current into heat through resistance.
Thermistor Tubular Heaters: These are tubular heaters that rely on changes in resistance with temperature variations. As temperature increases, resistance decreases, and vice versa.
Radial Tubular Heaters: Tubular heaters that can be designed in different sizes and provide resistance based on the direction of fluid flow.
Axial Tubular Heaters: Tubular heaters that provide resistance when fluid flows horizontally.
Thermostatic Tubular Heaters: Tubular heaters that can be used with temperature control systems and can change their resistance when a specific temperature value is reached.
This classification can vary depending on the application, working conditions, and requirements, and combinations of different types can also be utilized.
Tubular Heatings Technical Specifications
Operating Pressure: Maximum operating pressure refers to the maximum fluid pressure that the tubular heater can withstand. This is an important feature for the safe use of the tubular heater.
Operating Temperature: The operating temperature range indicates the temperature range in which the tubular heater can operate smoothly, covering both minimum and maximum temperatures.
Current Capacity: Current capacity denotes the maximum current that the tubular heater can carry within a specified time period. This feature ensures the safe operation of the heater.
Material: The material from which the tubular heater is made should be chosen based on the application’s requirements and the properties of the fluid. Materials such as stainless steel, nickel, and titanium are commonly used.
Dimensions: The dimensions of the tubular heater are determined based on the diameter, length of the pipe, and the requirements of the application. Proper sizing ensures effective performance.
Connection Types: Tubular heaters can have different types of connections, such as fixed or flexible connections. The type of connection should be selected based on the requirements of the application and the structure of the pipe.
These technical specifications are important for the proper selection and application of tubular heaters and may vary depending on the application field.